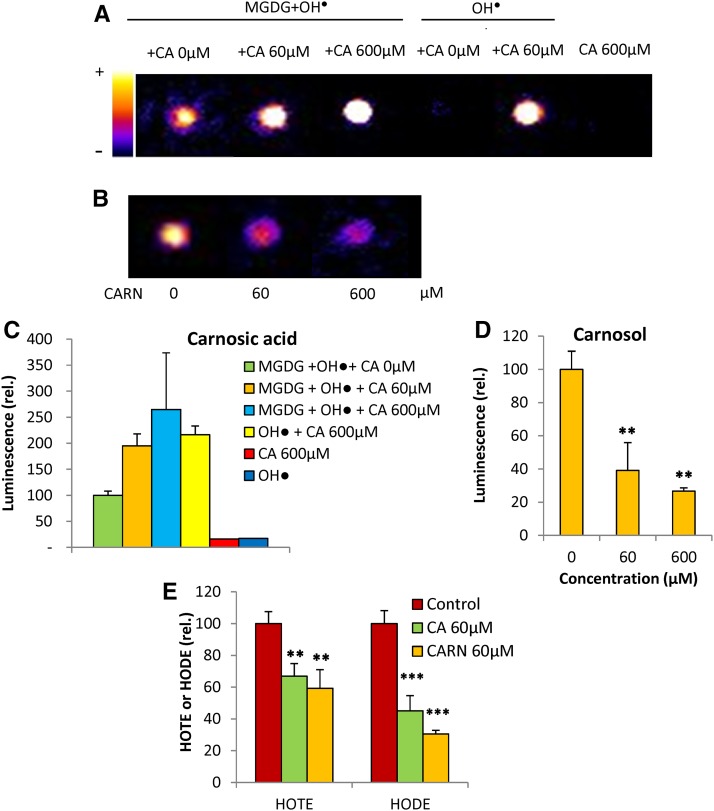
Figure 2.
Effects of carnosic acid and carnosol on in vitro oxidation of lipids by free radicals. Hydroxyl radicals were produced by the Fenton reaction using H2O2 + Fe2+ in the presence of 60 or 600 μm carnosic acid (CA) or carnosol (CARN). A, Luminescence imaging of MGDG oxidized by the hydroxyl radical in the presence or absence of carnosic acid (60 and 600 μm). The luminescence signals of the mixture H2O2 + iron (hydroxyl radicals) and of carnosol in the presence or absence of hydroxyl radicals also were measured as controls. B, Luminescence imaging of MGDG oxidized by hydroxyl radical in the presence of carnosol (60 and 600 μm). C, Quantification of the luminescence signals shown in A. Data are normalized to the signal values measured from oxidized MGDG in the absence of antioxidant. D, Quantification of the luminescence signals shown in B. Data are normalized to the signal values measured from oxidized MGDG in the absence of antioxidant. E, Hydroxy fatty acid quantification (HOTE and HODE). Data are normalized to the HOTE or HODE values measured in the absence of antioxidant. Asterisks indicate significant differences from control at P < 0.01 (**) and P < 0.005 (***) by Student’s t test.