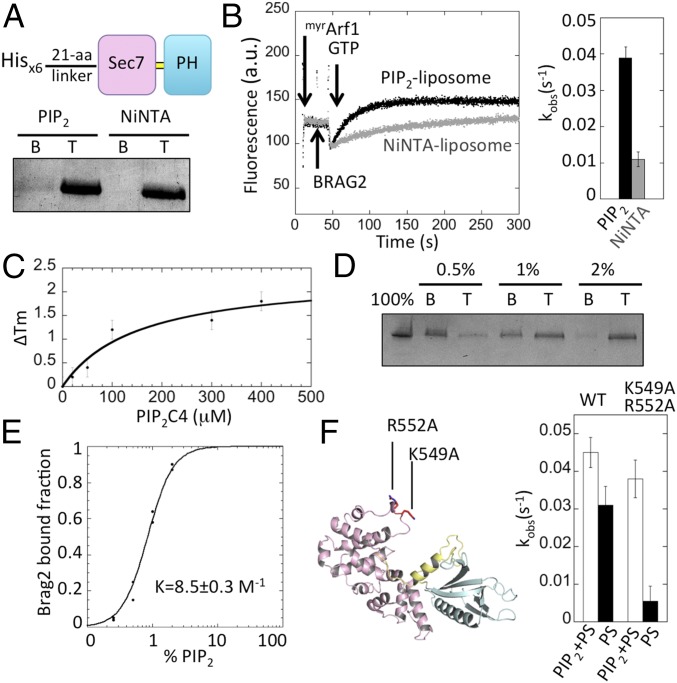
Fig. 4.
Interaction of Brag2 with PIP2 and PIP2-containing membranes. (A) Flotation analysis of the interaction of Brag2 with liposomes. The His-tagged construct used in this experiment is depicted. Liposomes contained either PIP2 or NiNTA lipids. B, bottom fraction, containing unbound proteins; T, top fraction, containing liposome-bound proteins. (B) Fluorescence kinetics trace showing the GEF activity of Brag2 (2 nM) toward myristoylated Arf1 (0.4 µM) in the presence of 100 µM PIP2 liposomes (black) or NiNTA liposomes (gray). The histogram shows the corresponding kobs values. (C) Analysis of binding of Brag2 to PIP2-C4 using a thermal shift assay. (D) Liposome flotation analysis of the interaction of Brag2 with liposomes containing increasing PIP2 concentrations. (E) Fraction of liposome-bound Brag2 as a function of PIP2 concentration. The Hill plot analysis shown in Fig. S5A indicates that PIP2 lipids bind to Brag2 in a positively cooperative manner. (F) Analysis of the GEF efficiency on membranes of Brag2 carrying mutations in the Sec7 domain. Liposomes contained either PIP2 or PS as a source of anionic lipids. The position of the mutations in the Sec7 domain is shown. Composition of liposomes is given in Table S2.