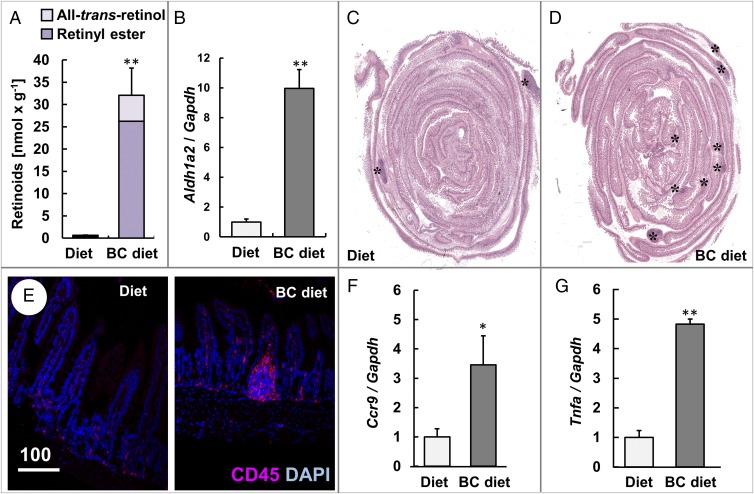
Fig. 2.
β-Carotene supplementation increases the number of lymphocyte follicles, lymphocyte marker protein, and the proinflammatory cytokine. Four-week-old Isx−/− mice were fed with either diet or β-carotene (BC) supplemented diet. (A) Retinoid content of the intestines. (B) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of jejunal Aldh1a2 mRNA levels. (C and D) Representative H&E-stained cross section through the intestine. The asterisks (*) indicate the location of lymphoid follicles. (Magnification: 20×.) (E) Intestinal cross section immunostained for CD45 (red). Nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue). (Scale bar, 100 µm.) (F and G) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of jejunal (F) Ccr9 and (G) Tnfa mRNA levels. Values in A, B, F, and G indicate mean ± SD of results from five animals per supplementation group. Threshold of significance was set at *P < 0.05 or **P < 0.01.