Fig. 2. None of MLCK, inhibitory peptides of calmodulin, or MLCK and EGTA affects MLC20 phosphorylation.
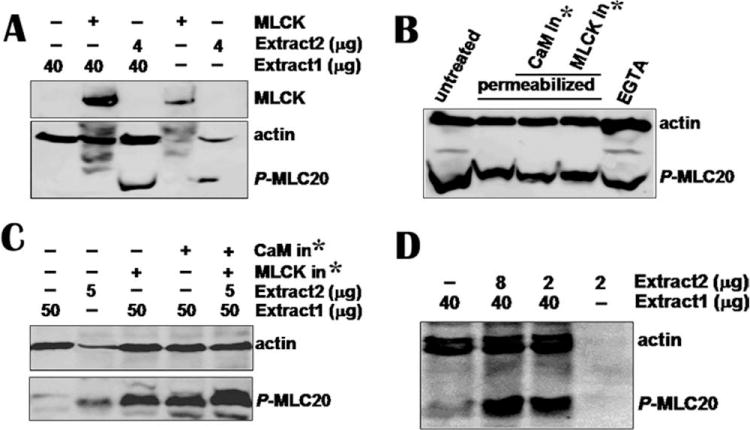
(A) Immunoprecipitated MLCK from 100 μg tissue was added to tissue extract 1 containing low −p-MLC20 and MLCK (Line 2). The immunocomplex beads containing MLCK from 50 μg tissue was loaded onto line 4. Reaction was stopped after 1-h incubation at 30°C by loading buffer and reaction mixture was loaded onto SDS-PAGE gel. Antibodies against p-MLC20 and actin were used to detect membranes. Western blotting shows that immunoprecipitated MLCK did not trigger phosphorylation of MLC20 in tissue extract 1 containing low phosphor-MLC20 (p-MLC20) and low MLCK (Line 2). However, 4 μg extract 2 containing high p-MLC20 and no detectable MLCK phosphorylated MLC20 (line 3). (B) Permeabilized hBSM cells were treated with calmodulin and MLCK inhibitory peptides (1000 nM each) for 3 h. EGTA (20 mM) was incubated with cells for 2 h. Cells were harvested for Western blotting and mixture of antibodies for p-MLC20 and actin was used to detected membranes. No significant inhibition on MLC20 phosphorylation was observed. (C) CaM and MLCK inhibitors did not inhibit MLC20 phosphorylation when they were incubated with smooth muscle extracts. (D) Small amount of high p-MLC20 without detectable MLCK tissue catalyzed MLC20 phosphorylation in low p-MLC20 and MLCK tissue extract. *CaM or MLCK inhibitor.
