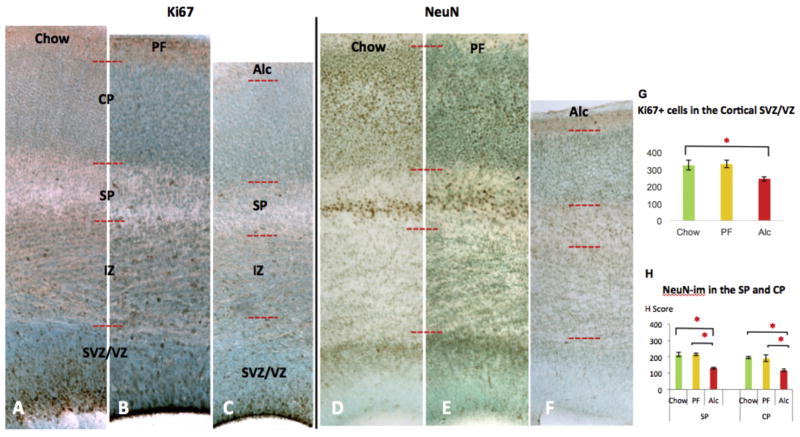
Fig. 5.
Alcohol-induced changes of Ki67-im and NeuN-im across different groups of E17 cortices. Representative cortical column of E17 Chow (A, D), PF (B, E), and (C, F) Alc group coronal sections for Ki67 and NeuN immunostaining. Fetal alcohol-induced reduction of Ki67 immunoreactivity was observed mainly in the SVZ/VZ zone, the neuroepithelial cellular zones. Quantitative assessment of Ki67-im (+) cells further confirmed an alcohol-related reduction in the SVZ/VZ zone (G); N = Chow (5), PF (4), Alc (7). Alcohol reduced NeuN-im throughout cortical SP and CP layers (F) compared to Chow (D) and PF (E). No significant change was observed between Chow and PF groups. Quantitative assessment of NeuN-im was further quantified by single-cell density analysis (H Scoring) across the three groups (H). *p < 0.05. Data are mean ± SEM. VZ/SVZ (Ventricular Zone/Subventricular Zone); IZ (Intermediate Zone); SP (Subplate); CP (Cortical plate).