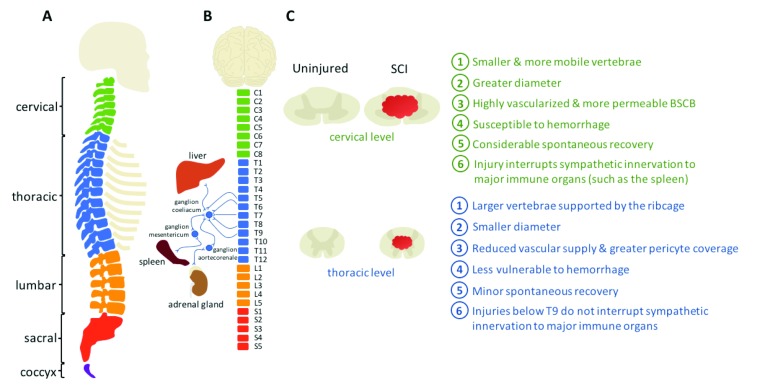
Figure 1. There are several key differences between cervical and thoracic spinal cord injury.
( A) The cervical vertebrae are smaller and more mobile than their thoracic counterparts, which are further supported by the rib cage. ( B) The cervical spinal cord also has a larger diameter, and injuries at the cervical level interrupt the sympathetic innervation to major immune organs. ( C) Moreover, the greater vascularity of the cervical cord increases susceptibility to hemorrhage following trauma. Lastly, injuries at the cervical level allow for considerably more spontaneous recovery compared with injuries at the thoracic level 128. BSCB, blood spinal cord barrier; SCI, spinal cord injury.