Figure 1.
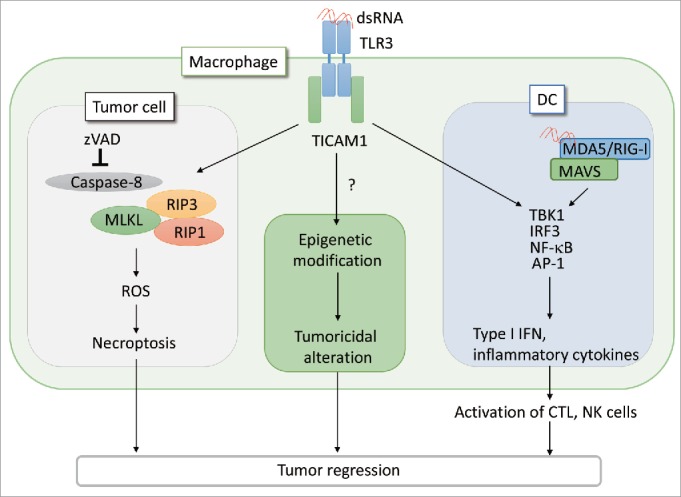
PolyI:C induces tumor necroptosis via the TLR3 -TICAM1 pathway. When CT26 cells are treated with pan-caspase inhibitor, zVAD, the interaction of TICAM1 and RIP3 is enhanced in response to poly(I:C), leading to cell death by necroptosis. In the absence of immune cells, this necroptosis pathway contributes to tumor regression in vivo. Necroptosis is induced in macrophages stimulated with poly(I:C).2 Poly(I:C) also acts on DCs and macrophages to elicit effective CTL/NK activation and modify tumor microenvironment, respectively, as previously reported.4-6 The antitumor response of TLR3 appears to be cell type-specific. Notably, tumor-infiltrated macrophages harbor all the signal axes inducible by poly(I:C)/TLR3 as illustrated. The functional alteration of macrophages may be associated with epigenetic status of the cells in inflammatory environment.
