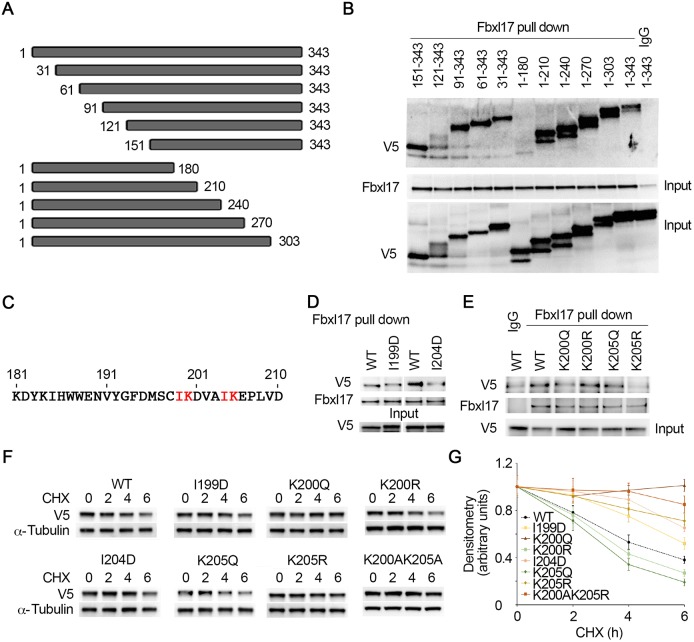
Fig. 4.
Fbxl17 docks on an IKxxxIK motif within PRMT1 and the acetylation status of the lysine residues in the motif is crucial for Fbxl17 binding. (A) Schematic presentation of truncated PRMT1 mutants. (B) V5-tagged PRMT1 truncated mutants were synthesized in TnT reticulocyte lysate systems. HeLa cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with Fbxl17 antibody. In vitro binding assays were performed by mixing PRMT1 mutants and Fbxl17 beads for 2 h, and Fbxl17 pulling down precipitates were analyzed with V5 and Fbxl17 immunoblotting. (C) Amino acid sequence 181–210 of PRMT1. The IK residue sequences are indicated in red font. (D) Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with Fbxl17 antibody and then mixed with in vitro-synthesized V5-tagged WT or mutant (I199D and I204D) PRMT1 proteins for 2 h. The eluted proteins were subjected to V5 and Fbxl17 immunoblotting. The in vitro-synthesized recombinant proteins were analyzed with V5 antibody. (E) Endogenous Fbxl17 were obtained with Fbxl17 antibody immunoprecipitation. The protein-A/G agarose beads associated Fbxl17 were incubated with in vitro-synthesized V5-tagged WT, K200Q, K200R, K205Q and K205R mutant PRMT1 for 2 h. The pull-down proteins were immunoblotted with V5 and Fbxl17 antibodies. The in vitro-synthesized recombinants were analyzed with V5 antibody. (F,G) V5-tagged WT and mutant PRMT1 were introduced in to MLE12 cells for 24 h. The cells were treated with CHX (40 µg ml–1) for the indicated times and cell lysates were subjected to immunoblotting analysis with antibodies against V5 and α-tubulin. The immunoblots were analyzed by densitometry and plotted, respectively, in G. The results are representative of n=3 experiments.