Fig. 1.
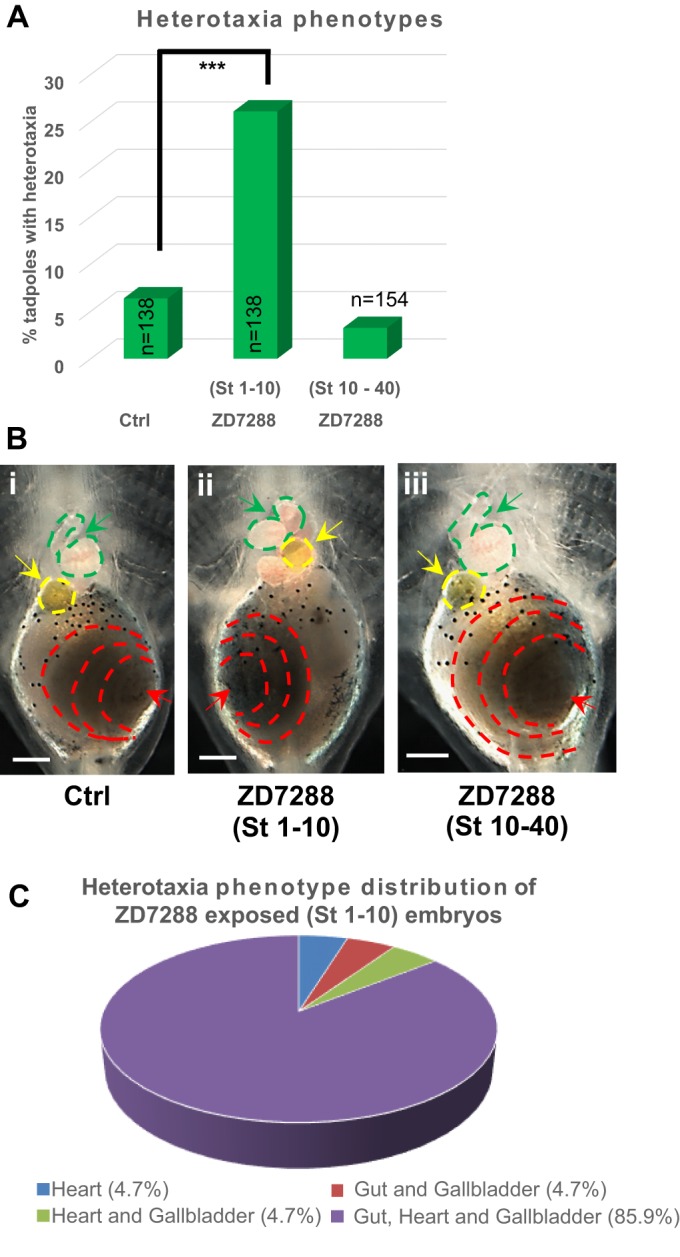
HCN4 channel inhibitor ZD7288 affects left-right organ laterality only upon early exposure of embryos (St 1-10). (A) Quantification of stage 45 tadpoles for left-right organ (heart, gut and gallbladder) laterality with or without exposure to 100 µM ZD7288 at 22°C at the indicated stages. A significantly high incidence of heterotaxia was observed in embryos exposed to ZD7288 between stages 1-10 in comparison to controls. Embryos exposed to ZD7288 late (St 10-40) did not show any significant increase in the incidence of left-right organ misplacement. The experiment was conducted in triplicates and data was pooled to run a χ2 analysis, ***P<0.001. (B) Representative images of stage 45 tadpoles: (i) Control tadpole showing rightward coiling gut as indicated by the red dotted lines and red arrow, rightward coiling heart as indicated by green dotted lines and green arrow, and leftward placed gallbladder as indicated by yellow dotted line and yellow arrow, (ii) tadpoles from embryos exposed to ZD7288 (100 µM – St 1-10) showing inversion of gut coiling as indicated by the red dotted lines and red arrow, inversion of the heart as indicated by green dotted line and green arrow, and inversion of gallbladder placement as indicated by yellow dotted lines and yellow arrow, (iii) tadpoles from embryos exposed to ZD7288 (100 µM – St 10-40) showing normal gut coiling as indicated by the red dotted lines and red arrow, normal heart as indicated by green dotted line and green arrow, and normal gallbladder placement as indicated by yellow dotted lines and yellow arrow. Scale bar: 0.25 mm. (C) Pie chart showing the incidence of various left-right phenotypes seen in the tadpoles from embryos exposed to ZD7288 (100 µM) between stages 1-10.
