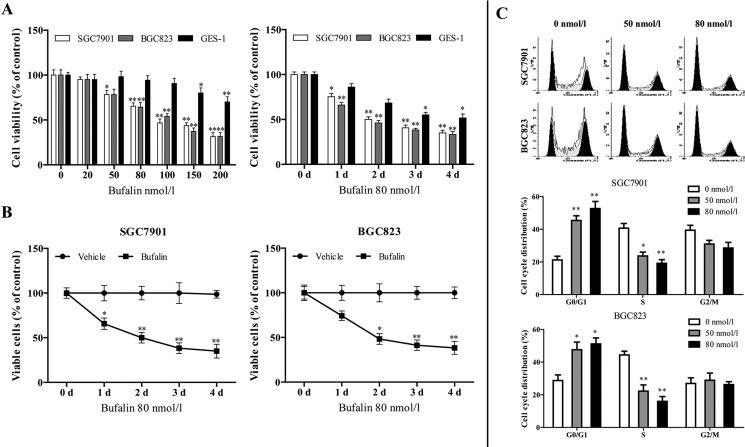
Fig. 1.
Bufalin suppressed proliferation of HGC cells and induced their cell cycle arrest. (A) HGC cells and a normal gastric mucous epithelium cell, GES-1, were treated with 20, 50, 80, 100, 150 and 200 nmol/l of bufalin or vehicle as control for 48 h, or 80 nmol/l of bufalin for 0, 1, 2, 3 and 4 days. Cell viability was determined using a CCK-8 assay. (B) Trypan Blue assays were performed to determine the anti-proliferative effect of bufalin on SGC7901 and BGC823 cells. (C) HGC cells were treated with 50 and 80 nmol/l of bufalin or vehicle as control for 48 h. The cell cycle distribution was determined using flow cytometric analysis and cell cycle distribution was quantified. *P<0.05 versus control treatment, **P<0.01 versus control treatment, Student's t-test. Data are presented as mean±s.e.