Fig. 7.
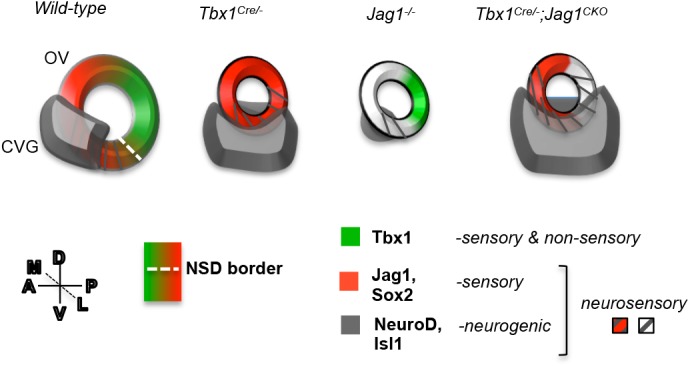
Model summary. A schematic of the OV summarizing the expression of the key genes of this study in the OV that is oriented as shown (dorsal-ventral, D-V; medial-lateral, M-L; anterior-posterior, A-P). In wild-type embryos at E10-10.5, Tbx1 is expressed at the NSD border marked by overlapping expression of neurogenic genes (grey stripes) and Jag1/Sox2 (red) in the anteroventral OV. This NSD is positioned adjacent to the developing CVG, marked by NeuroD and Isl1 expression (grey), and contributes to it some of its progenitor cells fated to become neurons. When Tbx1 is homozygously inactivated (Tbx1Cre/−), Jag1 expression is expanded throughout the OV, disrupting the NSD border. The CVG also expands into the posterior and lateral domain in Tbx1Cre/− (or Tbx1−/−) OVs. When Jag1 is inactivated (Jag1−/−), the Tbx1 expression domain is unchanged, and the CVG is significantly smaller in size. When Jag1 is inactivated together with Tbx1 in the Tbx1 expression domain (Tbx1Cre/−;Jag1f/+ or Tbx1Cre/−;Jag1f/f – termed Tbx1Cre/−;Jag1CKO), the NSD border is disrupted and the CVG is further enlarged.
