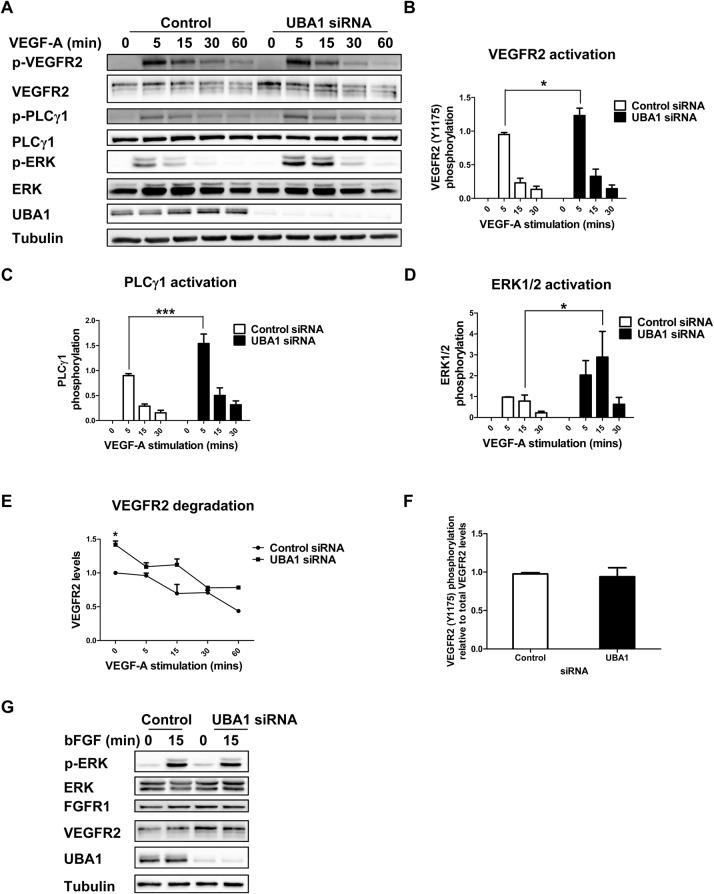
Fig. 5.
UBA1 depletion causes an increase in VEGF-A-stimulated signal transduction. (A) Endothelial cells transfected with non-targeting control siRNA or UBA1-specific siRNA were stimulated with 25 ng/ml VEGF-A for specific time periods (0-60 min), lysed and immunoblotted for phospho-VEGFR2 (Y1175), phospho-PLCγ1 (Y783), phospho-ERK1/2 (T202/Y204), VEGFR2, ERK1/2, UBA1 and tubulin. Quantification of (B) phospho-VEGFR2, (C) phospho-PLCγ1, (D) phospho-ERK1/2, and (E) VEGFR2 levels in endothelial cells transfected with non-targeting control siRNA or UBA1-specific siRNA and treated with 25 ng/ml VEGF-A for the time periods indicated. Relative levels for each signal were normalized against tubulin. (F) Quantification of phospho-VEGFR2 (Y1175) levels after 5 min VEGF-A stimulation and normalized against total VEGFR2 levels in control or UBA1-depleted endothelial cells. (G) Endothelial cells transfected with non-targeting control siRNA or UBA1-specific siRNA were treated with 25 ng/ml basic FGF (bFGF), lysed and immunoblotted for phospho-ERK1/2 (T202/Y204), VEGFR2, FGFR1, UBA1 and tubulin. In panels B-F, error bars denote mean±s.e.m. (n≥3), with significance denoted as *P<0.05, ***P<0.001; analysed using two-way ANOVA.