Fig. 1.
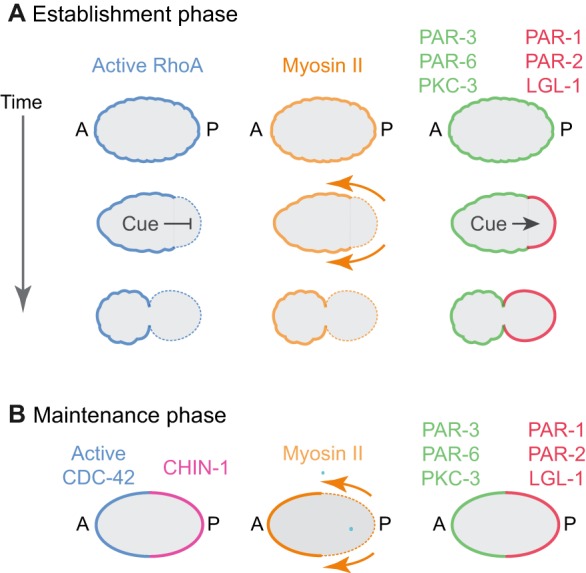
Overview of polarization in the C. elegans zygote. Polarization of the C. elegans zygote involves two distinct phases: establishment phase (A) and maintenance phase (B). (A) Before polarity establishment, anterior PAR proteins (green), active RhoA and Myosin II are uniformly enriched at the cell cortex. During polarity establishment, a transient sperm-derived cue acts locally to inhibit RhoA activity and induce actomyosin-based cortical flows that segregate anterior PAR proteins towards the anterior pole, and to promote local accumulation of posterior PAR proteins (red) on the posterior cortex where they act to inhibit local accumulation of anterior PAR proteins. (B) During maintenance phase, complementary distributions of anterior PAR proteins and posterior PAR proteins are maintained in the absence of a cue. RhoA activity is low, and CDC-42 activity becomes enriched at the anterior cortex, while the CDC-42 GAP CHIN-1 becomes enriched on the posterior cortex. CDC-42 acts through the kinase MRCK-1 to activate Myosin II on the anterior cortex, leading to persistent cortical flows.
