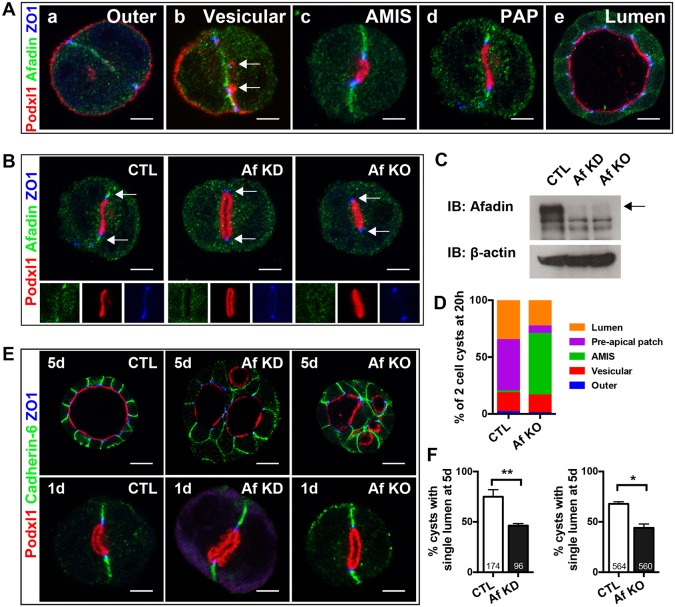
Fig. 2.
Afadin is required for timely lumen initiation and single lumen formation in MDCK cysts. (A) Afadin localization during cyst formation. (a) At the two-cell stage, afadin localizes to the cell-cell interface, ZO1 localizes to the lateral cell interface, and Podxl1 localizes to the outer periphery. (b) Podxl1 is internalized into vesicles (arrows) and transcytosed during lumen initiation to a site containing ZO1 but not afadin. (c) Afadin is absent from apical membrane initiation site (AMIS), but present at apical cell junctions (where it colocalizes with ZO1) and at the cell-cell interface. Afadin becomes restricted to apical cell junctions at the pre-apical patch (PAP) stage (d) and the open lumen stage (not shown), including later cysts, such as the 5-day cyst (e). At the apical cell junction, afadin partially colocalizes with ZO1, but some is basal to ZO1. (B,C) Immunofluorescence of afadin in 1-day cysts (B) and western blot of afadin in 5-day cysts (C) with shRNA-mediated afadin knockdown (KD) and CRISPR-Cas9-mediated afadin knockout (KO). (D) Quantification of the percentage of cysts at the indicated pre-luminal stages at 20 h. See text for details. (E) Immunofluorescence of Podxl1, cadherin 6, and ZO1 in 1-day and 5-day cysts with afadin KD and KO showing localization of these proteins. Cysts lacking afadin (KD and KO) have multiple lumens at day 5. (F) Quantification of the percentage of cysts with a single lumen at 5 days. Data are mean±s.d. There is a significant reduction in cysts with a single lumen in afadin KD (**P<0.002) and KO (*P<0.02) cysts. Results are representative of at least two independent experiments. Numbers at base of bars indicate the number of cysts analyzed. Scale bars: 5 µm (Aa-Ad,B,E upper panels); 10 µm (Ae,E lower panels).