Fig. 9.
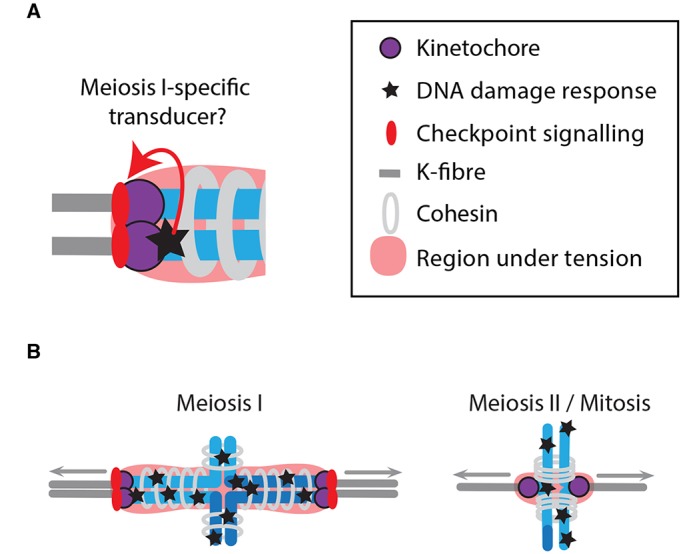
Model to explain meiosis I-specific SAC arrest following DNA damage. Possible mechanisms by which the SAC/DDR checkpoint functions specifically in meiosis I. (A) A meiosis I-specific protein could transduce a signal from sites of DNA damage in close proximity to the kinetochore to allow SAC signalling on the kinetochore; alternatively, this might happen due to the unique proximity of the two sister kinetochores in meiosis I. (B) The large volume of chromatin under tension during meiosis I might make the bivalent more sensitive to DNA damage compared with meiosis II or to mitosis.
