Fig. 1. Schematic drawing of the bacterial flagellar motor.
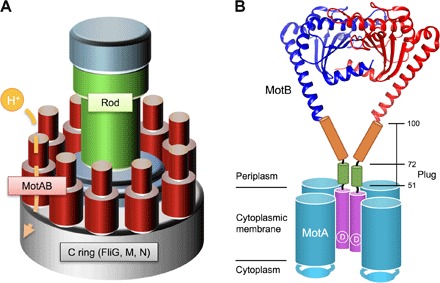
(A) Schematic diagram of the flagellar motor. The flagellar motor consists of a rotor ring complex and a dozen stator units made of two TM proteins, MotA and MotB. FliG, FliM, and FliN assemble into the C ring on the cytoplasmic face of the MS ring in this order and act as a rotor. (B) Schematic diagram of the MotAB complex. MotA and MotB together form a proton channel with four copies of MotA and two copies of MotB. Cα ribbon representation of the Salmonella MotBC structure (PDB code: 2ZVY) with the TM of MotAB and a flexible stalk of MotB (residues 51 to 100) connecting these two domains are shown. A highly conserved Asp33 residue (indicated as D) is directly involved in proton translocation through the MotAB proton channel complex. The stalk contains the plug segment (residues 53 to 66), which regulates the proton channel activity before stator assembly around the rotor.
