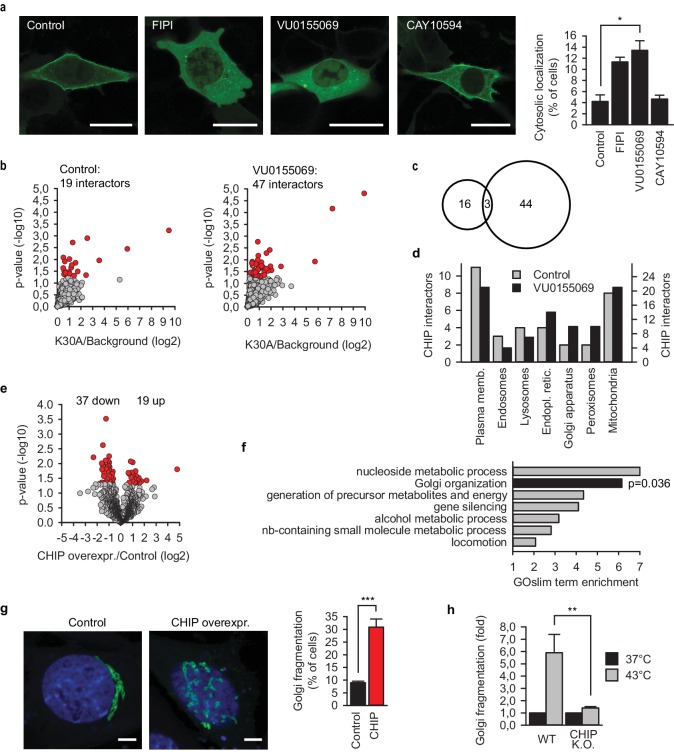
Figure 5. CHIP reorganizes cellular proteome and architecture.
(a) Inhibition of phospholipase D (PLD) releases EGFP-CHIP-K30A from cellular membranes. FIPI, isoform independent inhibitor of PLD; VU0155069 and CAY10594, inhibitors of PLD1 and PLD2, respectively. Scale bar 20 mm. *p<0.05, chi-square analysis; N = 4 independent experiments (mean ± SD). (b) Interactors of EGFP-CHIP-K30A in transiently transfected murine embryonic fibroblasts (MEF). Phospholipase D was inhibited using 500 nM VU0155069. EGFP pulldowns were prepared as detailed in Methods and label-free mass spectrometry was used to quantitate proteins associated with CHIP. N = 5 biologically independent experiments. Volcano plots indicate average enrichment of individual protein levels. Red color marks significantly enriched proteins as determined by two sample t-test (p-value<0.05) (c) Minimal overlap of CHIP interactors from control and upon phospholipase D inhibition visualized by a venn diagram. (d) Subcellular localization of CHIP interactors as assigned by GeneCards database (www.genecards.org). According to the database, proteins may display multiple localizations. The scales of y-axis were adjusted according to the interactome sizes (19 versus 47). (e) Label-free quantitative mass spectrometry was used to determine proteome changes in MEFs upon overexpression of CHIP for 24 hr (N = 4). Volcano plot indicates average changes of individual protein levels. Red color marks significantly changed proteins as determined by two sample t-test (p-value<0.05). (f) GOBPslim terms enriched above two in the group of proteins significantly changed upon CHIP overexpression. Fisher exact test was used to determine statistical significance. (g) Morphology of the Golgi apparatus upon transient CHIP overexpression in MEFs assessed by co-transfected Golgi marker. DAPI stain in blue. Scale bar 5 mm. ***p<0.001, chi-square analysis; N = 3 independent experiments (mean ± SD). (h) Fragmentation of Golgi apparatus during heat shock in wild-type (WT) and CHIP knock-out MEFs (CHIP K.O.). Fraction of cells with fragmented Golgi at 37°C was set to 1. Increase of cells with fragmented Golgi after 30 min at 43°C is plotted as mean ± SD from three independent experiments. **p<0.01, t-test analysis.