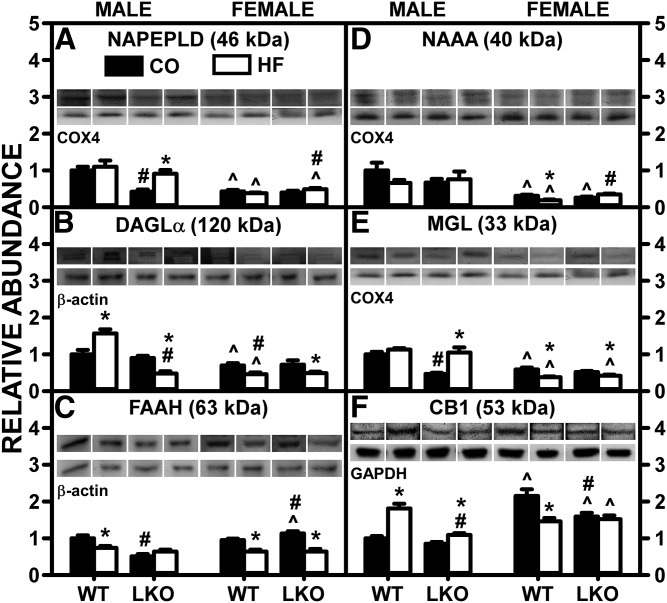
Fig. 6.
LKO differentially impacts the ability of HFD to alter liver protein levels of membrane proteins involved in EC synthesis and degradation. Male and female WT and FABP1 LKO mice on a C57BL/6N background were pair-fed a control diet (black bars, CO) or HFD (open bars, HF), as described in the Materials and Methods. All conditions were as in Fig. 4 except that Western blot analysis was performed, as described in the Materials and Methods, to determine protein levels of: NAPE-PLD (A), DAGLα (B), FAAH (C), NAAA (D), MGL (E), and CB1 (F). Relative protein levels were normalized to gel-loading control protein β-actin (FAAH and DAGLα), GAPDH (CB1), and COX4 (NAPE-PLD, NAAA, and MGL) and values compared with male WT set to 1. Mean ± SEM (n = 6–7). By ANOVA, *P ≤ 0.05 HFD versus control diet; #P ≤ 0.05 LKO versus WT on same diet; ^P ≤ 0.05 female versus male of same genotype and diet.