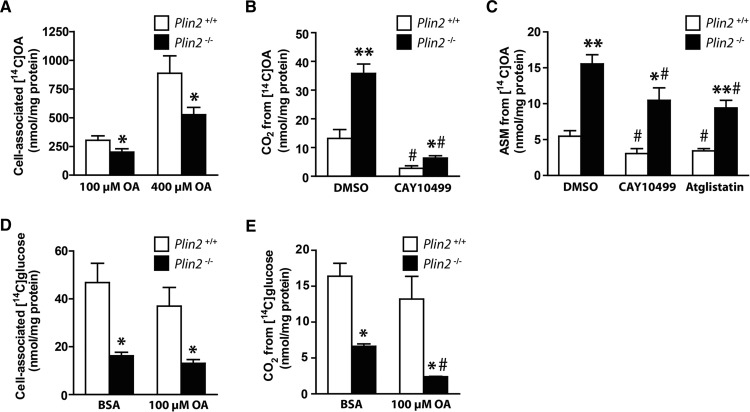
Fig. 5.
Cell-associated radioactivity and oxidation of OA and glucose in Plin2+/+ and Plin2−/− myotubes. For measurement of cell-associated radioactivity and oxidation of fatty acids (A–C), myotubes were preincubated with [1-14C]OA (100 or 400 µM) alone (0.1% DMSO) or in the presence of CAY10499 (10 µM) or Atglistatin (10 µM) for 24 h and then subjected to FA substrate oxidation assay for 4 h. A: Total cell-associated [14C]radioactivity remaining in Plin2+/+ and Plin2−/− myotubes after 4 h. B: Released CO2 arising from accumulated [14C]radioactivity after 4 h. C: FA intermediary oxidation products measured as [14C]radiolabeled ASMs released from the myotubes into the cell media during 24 h incubation with [14C]OA. The results are presented as means ± SEM (n = 3–7, *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 vs. Plin2+/+, #P < 0.05 vs. DMSO). For measurement of cell-associated radioactivity and oxidation of glucose (D, E), myotubes were preincubated with BSA (40 μM, i.e., basal) or OA (100 µM) for 24 h, before myotubes were incubated with D-[14C(U)]glucose and subjected to glucose substrate oxidation assay for 4 h. D: Total cell-associated [14C]radioactivity accumulated in myotubes after 4 h. E: Released CO2 from oxidation of D-[14C(U)]glucose. Results are presented as means ± SEM (n = 3–6, *P < 0.05 vs. Plin2+/+, #P < 0.05 vs. BSA).