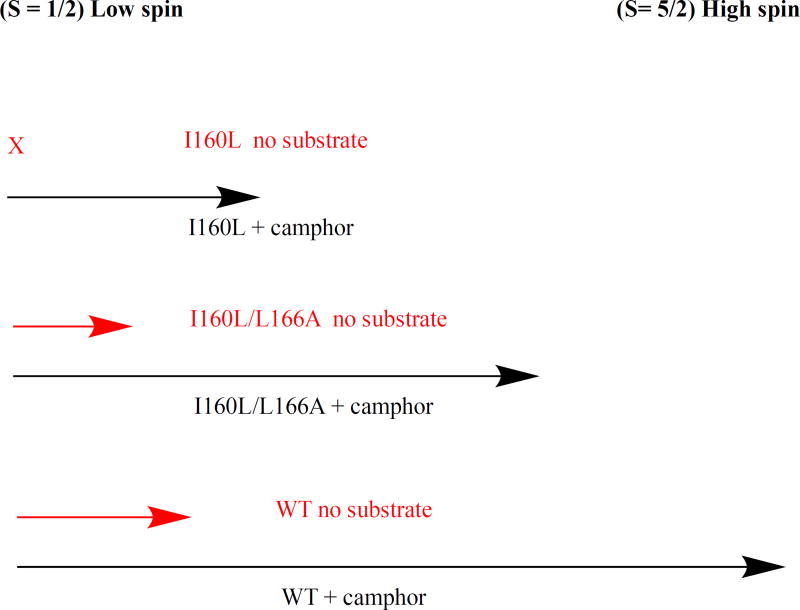
Figure 6.
Diagram of effect of substrate d-camphor 1 binding on spin state equilibrium in CYP101A1. Black arrows represent degree of high-spin (S= 5/2) ferric form (to the right on the diagram) upon binding of 1, while red arrows represent expected degree of high-spin form in the absence of substrate. Binding of 1 to WT CYP101A1 shifts conformational ensemble equilibrium in favor of > 95% high-spin. The I160L/L166A mutant binding of 1 shifts equilibrium to ~80% high-spin. Binding of 1 to I160L mutant shifts equilibrium less than 50% towards high-spin. Only WT and I160L/L166A have sufficient residual high-spin in the absence of 1 (ns = no substrate, red arrows) to support reduction of 6.