Figure 6.
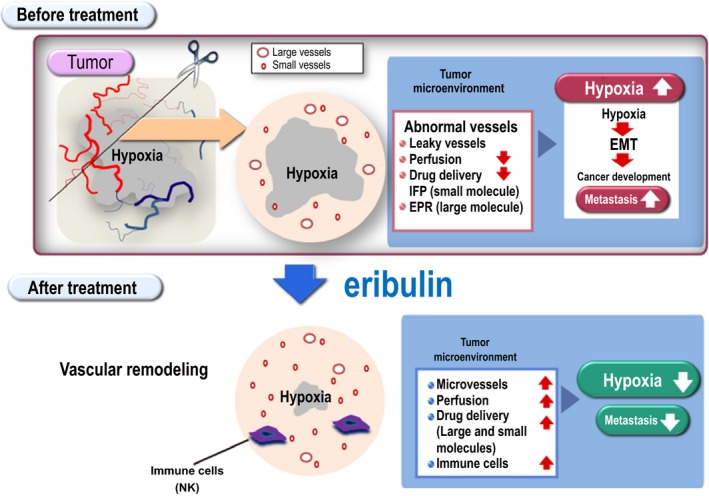
Role of eribulin as a tumor microenvironment modulator. Merits of the vascular remodeling effect are summarized in the schema. Our cumulative experimental results demonstrate that eribulin functions as a microenvironment modulator through increased drug accumulation (e.g. small molecule by reduced interstitial fluid pressure [IFP] and large molecule by enhanced permeability and retention [EPR] effect), increased infiltrating immune cells, as well as reduced hypoxic region. Collectively, these findings illustrate the significance of eribulin‐induced vascular remodeling effect for cancer treatment in multiple mouse xenograft models. EMT, epithelial to mesenchymal transition.
