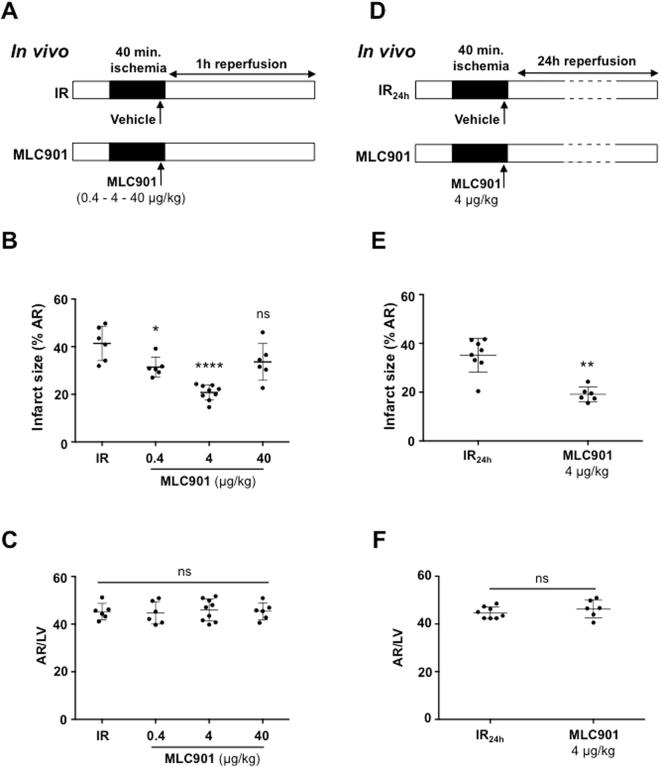
Figure 1.
Cardioprotection induced by MLC901 in vivo at the acute phase of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion. (A,D) Experimental protocols: mice underwent a surgical protocol of myocardial 40 min-ischemia followed by 1h-reperfusion (IR; panel A) or 24h-reperfusion (IR24h; panel D). Injection of MLC901 (0.4, 4 or 40 µg/kg) was performed intravenously 5 minutes before the onset of reperfusion. Infarct size measurement was performed at the end of reperfusion. (B) Scatter dot blots and means ± SD were plotted for infarct size (in % of area at risk). When mice were treated with MLC901 at 4 µg/kg, a 49.8%-decrease in infarct size was observed. A smaller cardioprotective effect was observed for the treatment with 0.4 µg/kg MLC901. This cardioprotective effect was not observed with 40 µg/kg MLC901. (C) Scatter dot blots and means ± SD were plotted for AR/LV mass. (D) IR24h animals received MLC901 (4 µg/kg) or physiological saline serum alone (IR). (E) Scatter dot blots and means ± SD were plotted for infarct size (in % of area at risk). (F) Scatter dot blots and means ± SD were plotted for AR/LV mass. Statistical analysis was performed using ANOVA test with the Tukey’s post hoc test for multiple comparisons or Mann-Whitney test for comparisons between 2 groups.