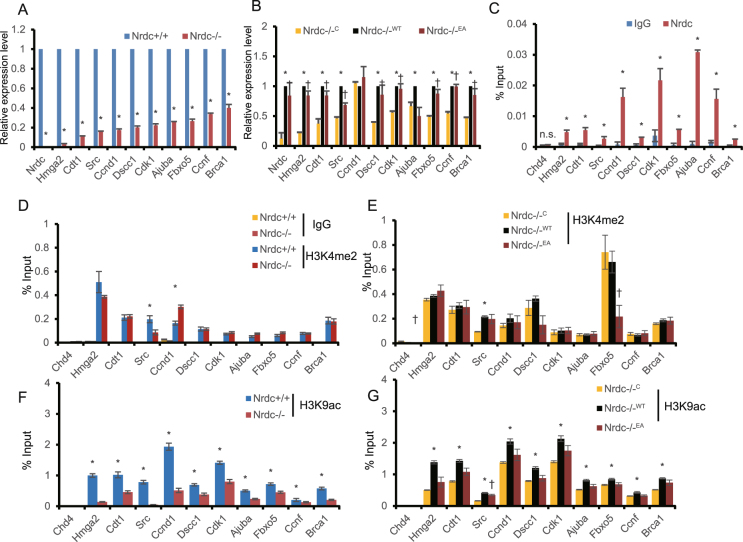
Figure 3.
Nrdc transcriptionally regulates cell cycle-associated genes via the modulation of histone acetylation. (A, B) RT-PCR of the indicated cell cycle-associated genes in Nrdc+/+ and Nrdc−/− iMEF (A), and in Nrdc−/−C, Nrdc−/−WT, and Nrdc−/−EA iMEF (B) (n = 3 per group). (C) ChIP-PCR using anti-Nrdc or control IgG shows Nrdc enrichment at the promoters of the indicated Nrdc direct targets in Nrdc+/+ iMEF (n = 3 per group). (D,E) ChIP-PCR analysis using anti-H3K4me2 and control IgG in Nrdc+/+ and Nrdc−/− iMEF (D), and in Nrdc−/−C, Nrdc−/−WT, and Nrdc−/−EA iMEF (E) for the promoters of the indicated Nrdc target genes (n = 3 per group). (F,G) ChIP-PCR using anti-H3K9ac in Nrdc+/+ and Nrdc−/− iMEF (F), and in Nrdc−/−C, Nrdc−/−WT, and Nrdc−/−EA iMEF (G) for the promoters of the indicated Nrdc target genes (n = 3 per group). All error bars indicate the standard error (S.E). *Indicates p < 0.05 between either Nrdc+/+ v.s. Nrdc−/− or Nrdc−/−C v.s. Nrdc−/−WT. †Indicates P < 0.05 Nrdc−/−C v.s. Nrdc−/−EA.