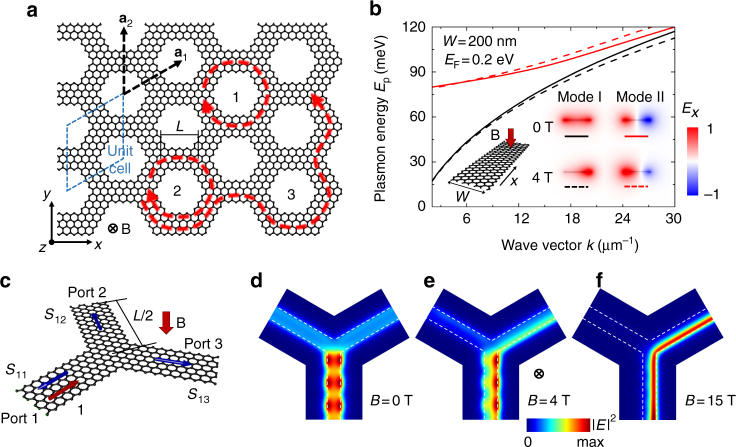
Fig. 1.
Topologically protected plasmons in a graphene superlattice. a Illustration of a honeycomb graphene superlattice with 100% right-coupling efficiency at each junction. Plasmons form localized vortex modes (1 and 2) and a unidirectional topologically protected edge state (3). b Dispersion relations of the two lowest-order modes sustained by a graphene nanoribbon (width W = 200 nm, Fermi energy E F = 0.2 eV) with and without a normal static magnetic field B (inset: schematic and electric-field distributions of guided modes for plasmon energy E p = 0.1 eV). c Schematic of a graphene nanoribbon junction with plasmons incident from branch 1 (unit incident amplitude), and scattered toward the three branches 1–3 with coefficients S 1,2−3. d–f Electric-field distributions (50 nm above graphene for E p = 0.06 eV) produced by plasmon scattering at the nanoribbon junction with and without magnetic field, assuming the same ribbon parameters as in b and neglecting inelastic losses. Dashed lines delineate the graphene edges