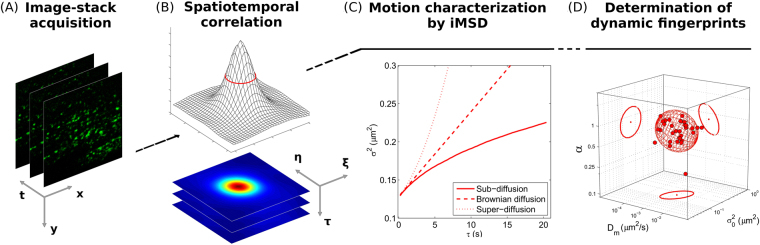
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the iMSD-based dynamic fingerprint analysis. (A) A stack of images of fluorescently-labelled intracellular structures is acquired by time-lapse confocal microscopy. (B) Spatiotemporal correlation function is derived from image analysis by the iMSD algorithm (see Materials and Methods for equations). (C) Gaussian fitting of correlation functions allows to extract the iMSD plot, which in turn depicts the average diffusion law of the structure of interest (exemplary cases are reported: super-diffusion, dotted red line; isotropic diffusion, dashed red line; sub-diffusion, solid red line). (D) Three relevant parameters are chosen from the fitting equation (see Materials and Methods) to quantitatively describe the average dynamic properties of the structure of interest, namely: the short-range diffusion coefficient (Dm), the anomalous diffusion coefficient (α), and the y-axis intercept of the iMSD plot, indicating the average size of the diffusing structures. These three parameters are organized in a 3D plot, used to identify the ‘dynamic fingerprint’ of the diffusing structure.