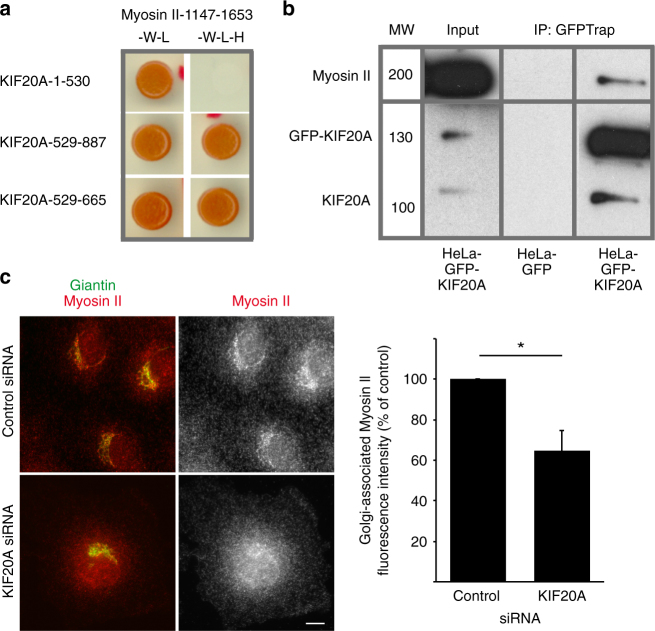
Fig. 3.
KIF20A interacts with Myosin II and stabilizes Myosin II at the Golgi. a Yeast two-hybrid interactions between the tail domain of Myosin II (1147–1653 fragment) and different domains of KIF20A. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae reporter strain L40 was co-transformed with a plasmid encoding fusion proteins to detect interactions between amino acids 1147 and 1653 of human myosin IIA heavy chain and the motor domain (1–530), the tail domain (529–887), and the RAB6 binding domain (RBD) (529–665) of KIF20A. Growth on medium lacking histidine (-W -L -H) indicates an interaction between the encoded proteins. b Endogenous Myosin II is pulled-down by GFP-KIF20A. GFP-KIF20A or GFP-transfected HeLa cell extracts were immunoprecipitated using the GFP-trap system. Myosin II bound to GFP-KIF20A was revealed by western blot analysis using anti-Myosin II antibody. GFP-KIF20A and KIF20A were revealed by anti-KIF20A antibody. Note that endogenous KIF20A is found in the IP fraction because it likely can form dimers with GFP-KIF20A. Input represents a 5% load of the total cell extracts used in all conditions. c Staining for endogenous Giantin (green) and endogenous Myosin II using the AD7 antibody (red) in Rat Clone 9 cells 3 days after transfection with specific KIF20A siRNAs. Bar, 10 µm. Of note, KIF20A is required for cytokinesis and KIF20A depletion leads to binucleated cells56,57. Quantification of Golgi-associated Myosin II fluorescence intensity in cells treated as described above (mean ± SEM, n = 23–66 cells). *P = 0.02 (Student’s t test). MW molecular weight in kDa