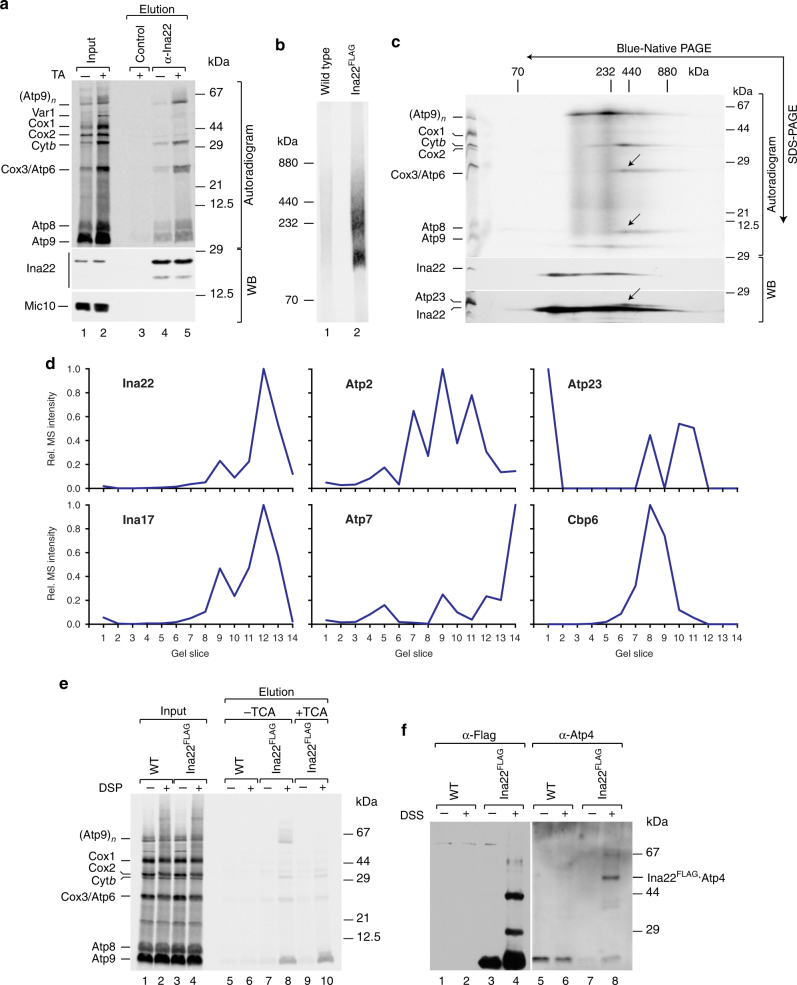
Fig. 6.
Ina22 interacts with mitochondrial-encoded F1F0-ATP synthase subunits. a Mitochondrial-encoded proteins in control and chloramphenicol-pretreated wild-type mitochondria were labeled in organello for 20 min. Proteins were co-immunoprecipitated with control or anti-Ina22 antibodies and samples were analyzed by SDS-PAGE, digital autoradiography, and western blotting (WB) with the indicated antibodies. Input = 1% of elution. TA, translational activation. b Chloramphenicol-pretreated wild type and Ina22FLAG mitochondria were subjected to in organello labeling, anti-FLAG affinity chromatography, and further analysis by BN-PAGE and digital autoradiography. c Part of the Ina22FLAG elution fraction of the experiment presented in b was subjected to BN-PAGE, second dimension SDS-PAGE, digital autoradiography, and western blotting (WB). Arrows indicate Atp6/Atp8 module, co-isolated with Ina22FLAG. d Ina22FLAG-containing protein complexes were immunopurified from Ina22FLAG mitochondria using anti-FLAG antibody. Eluates were analyzed by BN-PAGE and LC-MS followed by the establishment of protein abundance profiles. For each protein, summed MS intensities measured in each gel slice were calculated, the maximum intensity was set to 1, and normalized values were plotted across the 14 gel slices. e Wild type and Ina22FLAG mitochondria were subjected to chemical crosslinking after radiolabeling of mitochondrial-encoded proteins and Ina22FLAG was purified under denaturing conditions. Input and elution fractions were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and digital autoradiography. Elution fractions were split and either left untreated (lanes 5–8) or precipitated with 12.5% TCA to disrupt Atp9 oligomer (lanes 9–10). f Wild type and Ina22FLAG mitochondria were subjected to chemical crosslinking and Ina22FLAG was purified under denaturing conditions. Elution fractions were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and western blotting with anti-FLAG or anti-Atp4 antibodies