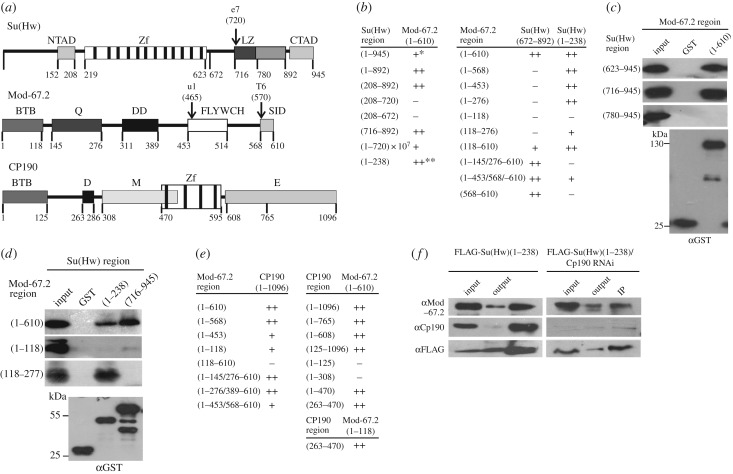
Figure 2.
Summary of interactions between domains of Mod(mdg4)-67.2, Su(Hw) and CP190 proteins. (a) Structural scheme of Su(Hw), Mod(mdg4)-67.2 (Mod-67.2) and CP190 showing the domains of these proteins and the corresponding numbers of amino acid residues. Domain abbreviations: NTAD, N-terminal acidic domain; CTAD, C-terminal acidic domain; Zf, zinc-finger domains; LZ, leucine zipper motif; BTB, BTB/POZ domain; Q, glutamine-rich (Q-rich) region; DD, dimerization domain; FLYWCH, FLYWCH-type zinc finger domain; SID, Su(Hw) interaction domain; D, aspartic acid-rich (D-rich) domain; M, centrosomal targeting domain; E, C-terminal glutamic acid-rich domain. Arrows indicate the location of the su(Hw)e7 (e7), mod(mdg4)u1 (u1) and mod(mdg4)T6 (T6) truncation alleles. (b) The results of testing Su(Hw) domains for the interaction with Mod-67.2 domains. All experiments were repeated in triplicate. Numbers in brackets are the numbers of amino acid residues. The plus signs indicate the relative strength of two-hybrid interaction (electronic supplementary material, figure S1b); the minus sign, the absence of the interaction; one asterisk, reduction in the interaction due to the repressive effect of the Su(Hw) C-terminal domain [73]; two asterisks, strong interaction observed only when DBD of GAL4 was fused to the C-terminal part of Su(Hw) derivatives. (c) Test for direct interaction between GST-fusion Mod(mdg4)-67.2 protein and His-fusion Su(Hw) domains in a GST pull-down experiment. (d) Test for direct interaction between GST-fusion Su(Hw) and His-fusion Mod(mdg4)-67.2 domains in a GST pull-down experiment. The interactions between the regions of insulator proteins were visualized by western blot analysis with anti-His tag monoclonal antibodies or with anti-GST antibodies used as loading control (at the bottom). The sample in the InPut lane contained 10% of His-fusion protein loaded onto Glutathione Sepharose together with GST-fusion insulator proteins. The sample in the GST column contained GST alone. Numbers in brackets are the numbers of amino acid residues. All results were reproduced in three independent experiments. (e) The results of testing Mod-67.2 domains for the interaction with CP190 domains. (f) Co-immunoprecipitation between the N-terminal domain of Su(Hw) fused to the FLAG epitope and insulator proteins under normal conditions and after CP190 RNAi treatment. The immunoprecipitated complexes were washed with 500 mM KCl-containing buffers before loading onto SDS-PAGE for western blot analysis with antibodies against the indicated proteins (CP190 or Mod-67.2) or the FLAG epitope. Input is the input fraction (10% of lysate used for immunoprecipitation); Output, the supernatant after immunoprecipitation; IP, the immunoprecipitate.