Figure 4.
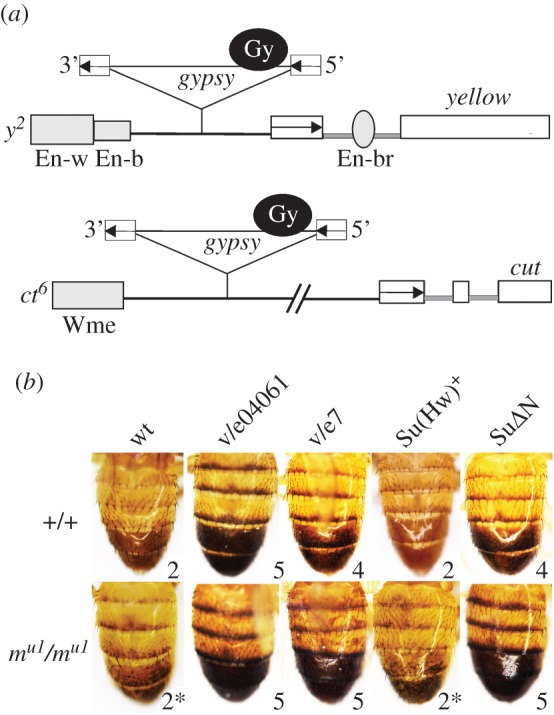
The functional role of multiple interactions between Mod(mdg4)-67.2 and Su(Hw) proteins. (a) Schemes (not to scale) of the y2 and ct6 alleles. Exons of the yellow and cut genes are shown as white rectangles; the yellow wing (En-w) and body (En-b) enhancers, as partially overlapping grey boxes; the bristle enhancer (En-br), as a grey oval in the yellow intron. The grey box (Wme) indicates the wing margin enhancer controlling cut expression in the wings. The transcription start sites are indicated by arrowheads. The gypsy insertions are shown as triangles in which the black circle marked Gy is the gypsy insulator and white boxes are long terminal repeats, with arrows indicating their direction. (b) Effect of Su(Hw) and its derivatives on the activity of the gypsy insulator in the y2 allele in the mod(mdg4)+ (+/+) or mod(mdg4)u1 (mu1/mu1) background. The names of alleles included in analysis are listed at the top: wild-type (wt) – y2scD1ct6, other designations are as in figures 1a and 3. Photos represent the abdominal pigmentation in 3-day-old males. Numbers indicate the scores of yellow expression in the body cuticle and wing blades, which ranged from 2 (pigmentation as in the y2 allele) to 5 (pigmentation as in wild-type flies). Asterisks indicate mosaic abdomen specific for the y2 allele on the mod(mdg4)u1 background.
