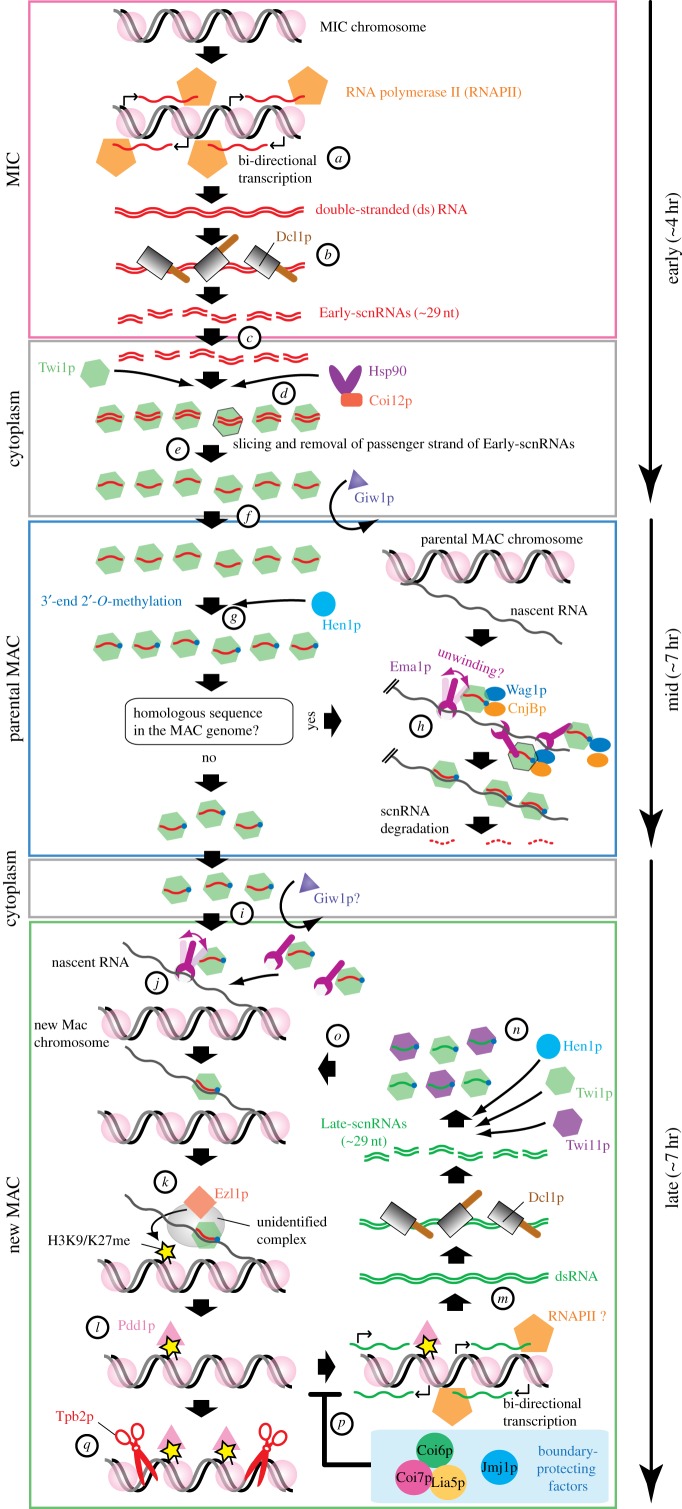
Figure 3.
Machinery of DNA elimination. Bi-directional transcription in the MIC by RNA polymerase II produces double-stranded RNAs (a), which are processed by the Dicer-like protein Dcl1p to Early-scnRNAs (b). Early-scnRNAs are exported to the cytoplasm (c) where they are loaded into the Argonaute protein Twi1p with the aid of Hsp90 and its co-chaperone Coi12p (d). The passenger strand of the Early-scnRNA duplex is cut and removed by the Slicer activity of Twi1p (e). Giw1p transports the Early-scnRNA–Twi1p complex to the parental MAC (f). The RNA methyltransferase Hen1p introduces 2′-O-methylation to the last nucleotides of Early-scnRNAs (g). The RNA helicase Ema1p facilitates the interaction between the Early-scnRNA–Twi1p complex and complementary nascent transcripts, which induce the degradation of Early-scnRNAs (scnRNA selection). Two GW-repeat proteins, Wag1p and CnjBp, are also necessary for scnRNA selection (h). The remaining Early-scnRNA–Twi1p complexes are transported into the new MAC, possibly by Giw1p (i). Like in the parental MAC, Ema1p facilitates the interaction between the Early-scnRNA–Twi1p complex and nascent RNAs (j). This interaction recruits the histone methyltransferase Ezl1p, which catalyses H3K9me3 and H3K27me3 (k). The HP1-like protein Pdd1p binds to these methylated histones (l). Heterochromatin induces bi-directional transcription in cis, resulting in Dcl1p-dependent production of Late-scnRNAs (m). Late-scnRNAs are loaded into Twi1p and Twi11p and then are 2′-O-methylated by Hen1p (n). The Late-scnRNA-Twi1/11p complex recruits Ezl1p, forming an RNAi-heterochromatin positive feedback loop (o). The feedback loop is downregulated by ‘boundary-protecting factors’ Coi6p (HP1-like), Coi7p, Lia5p (domesticated piggyBac transposase) and Jmj1p (H3K27 demethylase) (p). The domesticated piggyBac transposase Tpb2p eventually excises heterochromatinized IESs (q).