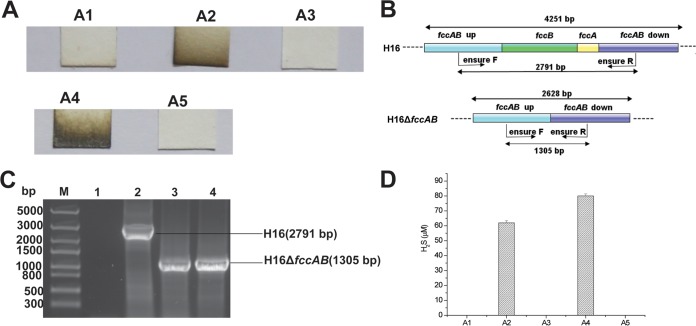
FIG 1.
Genetic analysis of fccAB in C. necator H16. (A) H2S production abilities of different bacteria. A1, C. necator H16; A2, C. necator H16 ΔfccAB; A3, C. necator H16 ΔfccAB/fccAB; A4, Pa3K; A5, Pa3K(pBBR5-fccAB). (B) Process for construction of C. necator H16 ΔfccAB. (C) Analysis of PCR fragments to confirm fccAB disruption. Lane M, molecular size standards; lane 1, product amplified with water as the template (negative control); lane 2, product amplified with C. necator H16 genomic DNA as the template; lane 3, product amplified with C. necator H16 ΔfccAB genomic DNA as the template; lane 4, product amplified with C. necator H16 ΔfccAB/fccAB genomic DNA as the template. The PCRs were performed with primers ensure F and ensure R. (D) Relative production of H2S in different strains. The data were generated by scanning and comparison to standards. The detection limit with the lead-acetate paper strips was about 5 μM.