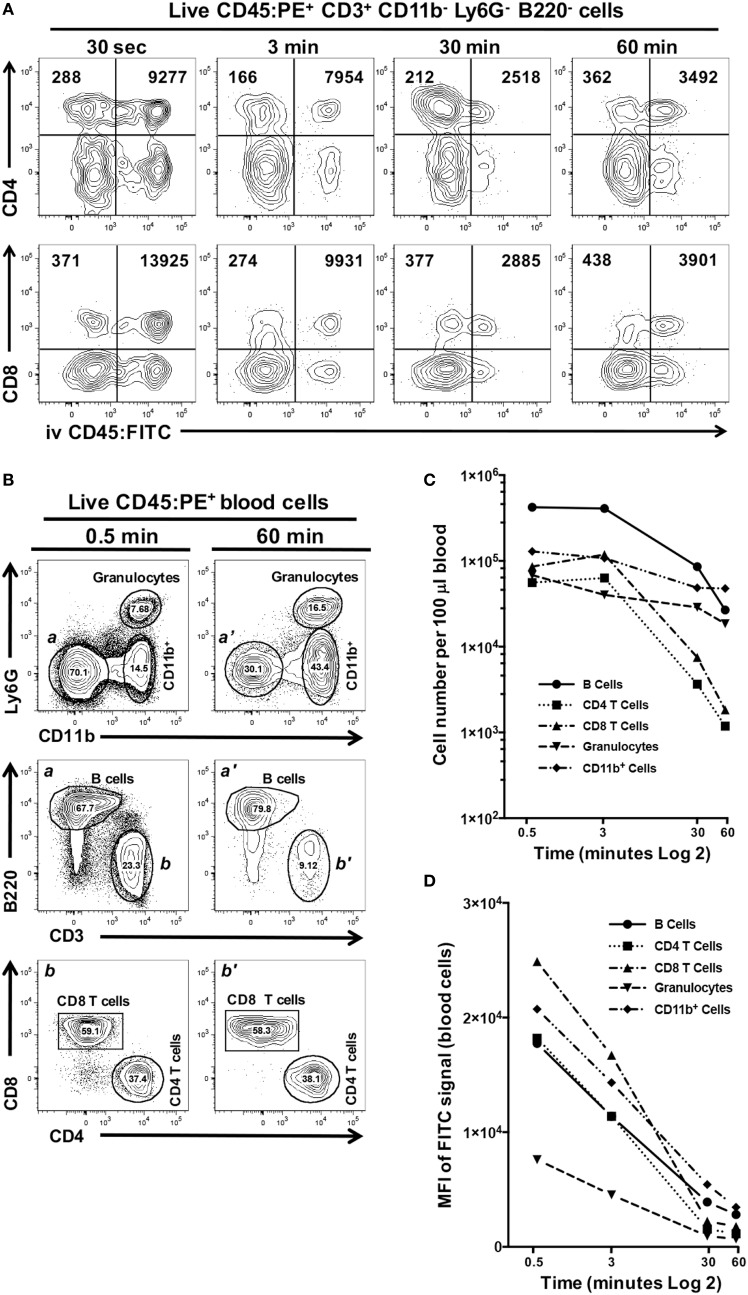
Figure 6.
Increased exposure time to intravenous anti-CD45 mAb results in poor discrimination between interstitial and circulating leukocytes. Anesthetized C57BL/6J mice were given 1.25 µg of CD45:FITC mAb in 200 µl of PBS via retro-orbital intravenous injection and mice were euthanized at 0.5, 3, 30, or 60 min. Separate blood and oral mucosa samples were pooled from three mice. Processed single-cell suspensions were stained with vitality dye Zombie NIR followed by rat anti-mouse CD45:PE, B220c, CD3, CD4, CD8, CD11b, and Ly6G mAbs to identify live immune cell subsets in blood and oral mucosa samples. (A) Representative dot plots are shown of live CD4 or CD8 T cells identified from mucosal samples taken at 0.5, 3, 30, or 60 min. Numbers in the upper two quadrants indicate the mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of the FITC signal found on cells within those quadrant populations. (B) Identification of CD11b+ cells and granulocyte, B cell [gates and panels a and a’], CD4 T cell, CD8 T cell populations [gates and panels b and b’] in pooled blood samples taken from mice at 0.5 or 60 min. Percentage of each population within a gate is given. (C) Number of live B cell, CD4 T cell, CD8 T cell, CD11b+, and granulocyte populations identified in 100 µl of blood samples taken at 0.5, 3, 30, or 60 min. (D) MFI of FITC signal found in the B cell, CD4 T cell, CD8 T cell, CD11b+, and granulocyte populations identified in 100 µl of blood samples taken at 0.5, 3, 30, or 60 min.