Figure EV2. Naloxone‐precipitated withdrawal signs in WT mice (n = 8/group) i.c.v. injected with AZD0530.
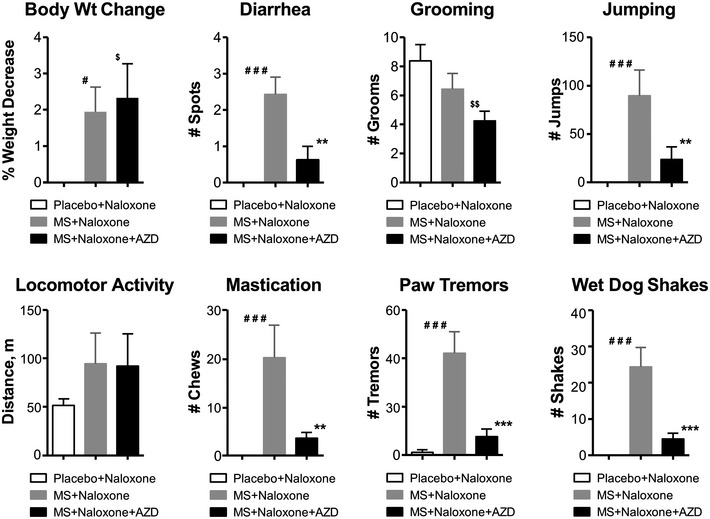
This presentation allows a comparative view of all the withdrawal signs including jumping presented in Fig 5A. The inhibition of Src activity after the i.c.v. injection of 50 μg of AZD0530, induces a significant decrease in naloxone‐precipitated diarrhea, jumping, mastication, paw tremors, and wet dog shakes (WDS). Body weight (Body Wt Change), grooming, and locomotor activity remain unchanged. Significant differences among the groups were determined using one‐way ANOVA, followed by Duncan's post hoc comparison. ***P < 0.001 and **P < 0.01 significant differences between the morphine‐and‐naloxone‐treated mice (MS + Naloxone, n = 8) and morphine‐naloxone‐and‐AZD‐treated mice (MS + Naloxone + AZD, n = 8). ### P < 0.001 and # P < 0.05 significant differences between the placebo‐and‐naloxone‐treated mice (Placebo + Naloxone, n = 8) and morphine‐and‐naloxone‐treated mice (MS + Naloxone). $$ P < 0.01 and $ P < 0.05 significant differences between the placebo‐and‐naloxone‐treated mice (Placebo + Naloxone) and morphine‐naloxone‐and‐AZD0530‐treated mice (MS + Naloxone + AZD0530). The bars and errors represent the means ± SEM. Exact P‐values are in Appendix Table S3.
