Figure 6. Restoration of naloxone‐precipitated somatic withdrawal signs in MOR −/− mice with WT MOR but not MORY336F lentivirus injected into the LC .
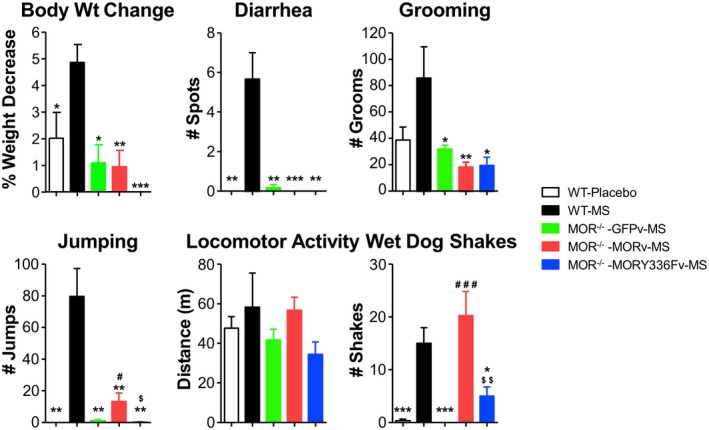
Construction of the lentiviruses containing the TH promoter that controls the expression of GFP (control), WT MORGFP, or MORY336F‐GFP was as described in the Materials and Methods. MOR−/− mice were stereotaxically injected with the GFPv (n = 6), MORv (n = 8), or MORY336Fv (n = 6) 1 week prior to chronic treatment with morphine and the subsequent monitoring of the naloxone‐precipitated somatic withdrawal signs as described. In parallel, chronic morphine treatment and naloxone‐precipitated withdrawal were carried out in WT mice (WT‐MS, n = 6). Placebo‐implanted WT mice injected with naloxone do not show withdrawal (WT‐Placebo, n = 6). The somatic withdrawal signs of body weight change, diarrhea, grooming, jumping, locomotor activity, and WDS were assessed for 30 min. Significant differences among the groups (MOR−/− ‐GFPv‐MS, MOR−/− ‐MORv‐MS, and MOR−/− ‐MORY336F‐MS) were determined using one‐way ANOVA, followed by Duncan's post hoc tests. ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01 and *P < 0.05 relative to WT‐MS; ### P < 0.001 and # P < 0.05 significant differences between MOR−/− ‐GFPv‐MS and MOR−/− ‐MORv‐MS; $$ P < 0.01 and $ P < 0.05 significant differences between MOR−/− ‐MORv‐MS and MOR−/− ‐MORY336Fv‐MS. The bars and errors represent the means ± SEM. Exact P‐values are in Appendix Table S1.
