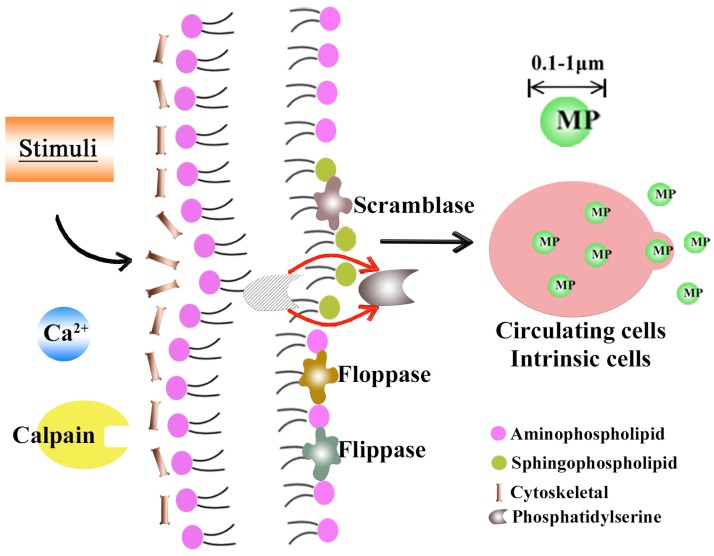
Figure 1.
The formation of MPs. When stimulated by external factors (e.g., inflammation, apoptosis), intracellular calpain and phosphatase are, respectively, activated and inhibited, reorganizing the cytoskeleton via three enzymes (flippases, floppases and scramblase) and phosphatidylserine (PS) exposure from the inner monolayer to the MP surface, all of which led to the final vesiculation and outward budding of the plasma membrane.