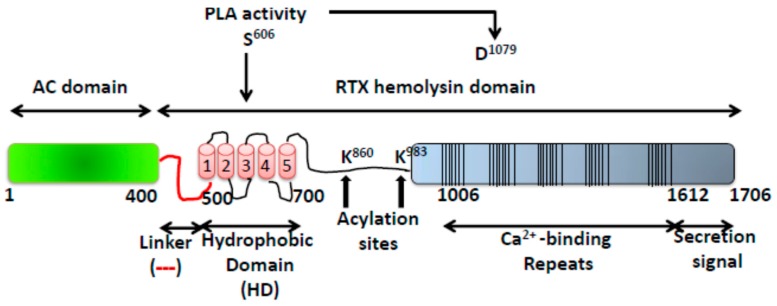
Figure 1.
Structural organization of the ACT toxin. The catalytic domain (AC domain) (in green) extends approximately from residues 1 to 400. The RTX haemolysin domain (residues from ≈500 to 1706) contains the hydrophobic domain (HD) constituted by five hydrophobic-amphipathic alpha-helices (in red), two conserved acylation sites, K860 and K983, required for activation by palmitoylation mediated by CyaC acyltransferase, and five blocks formed by low affinity calcium-binding repeats. The Ca2+-binding region (residues 1006–1612) is denoted by multiple lines, with each line corresponding to single nonapeptide repeats with consensus sequence GGXGXDXLX. The segment between residues 1638–1706) corresponds to the C-terminal secretion signal.