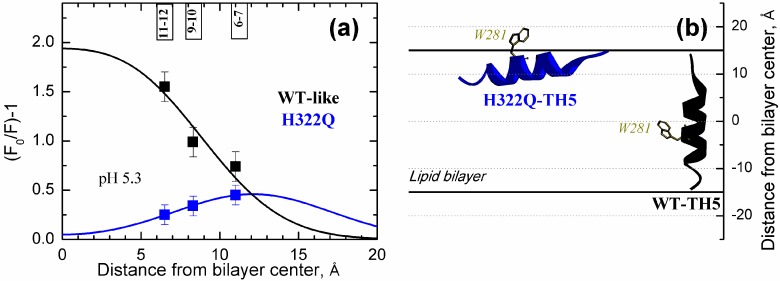
Figure 3.
Depth-dependent fluorescence quenching measurements of W281 in WT-like (black) and H322Q T-domain (blue) using brominated lipids (both T-domain constructs carry W206Y mutation). (a) Quantitative analysis of penetration of W281 into the lipid vesicles containing brominated lipids. Relative quenching efficiency, F0/F-1 (where F-fluorescence measured in the presence of bromolipids and F0-fluorescence without bromolipids) is plotted against the average distances of bromine atoms from the center of the bilayer (11.0 Å, 8.3 Å, and 6.5 Å for 6-7-dibromo-PC, 9-10-dibromo-PC, and 11-12-dibromo-PC, respectively [54]). Solid lines represent results of fitting with a simplified version of Distribution Analysis (Equation (1)) with the following parameters: hm = 4.5 ± 1.5 Å, S = 1.5 ± 0.3, and δ = 5.0 Å(fixed) for WT-like, and hm = 12.1 ± 0.1 Å, S = 0.46 ± 0.1, and δ = 5.0 Å(fixed) for H322Q. (b) Schematic illustration of the proposed topology of TH5 helix in the lipid bilayer for T-domain WT and H322Q, consistent with positioning W281 in accordance with the data in panel (a). The TH5 adopts transbilayer topology in the OCS conformation for the WT T-domain, and interfacial topology for the OCS-blocking H332Q mutant.