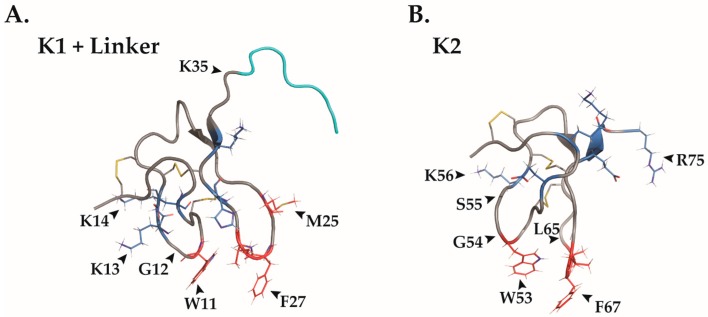
Figure 2.
The amphipathic nature of the DkTx structure allows it to protrude the membrane bilayer. Individually visualized knots of DkTx, with the linker (cyan) between the two knots appearing on K1 (A) Hydrophobic residues are labeled in red and polar residues in blue. This amphipathic nature presumably enables DkTx to successfully protrude into the lipid environment of the cell membrane. Key amino acids indicated in TRPV1 binding according to computational scan studies have been labeled (). Disulfide bridges are labeled in yellow. K1, PDB ID2N9Z. (B) K2 knot of DkTx labeled as described in A. Amino acids in K2 are numbered according to the molecule in its entirety.PDB ID: 2NAJ.