Figure 4.
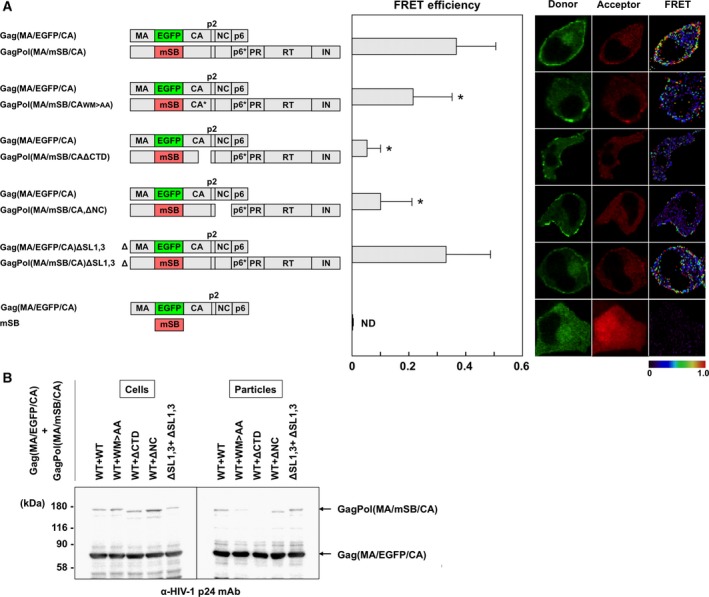
FRET assays for interactions of Gag and GagPol with mutations and virus particle production. (A) FRET efficiencies of Gag(MA/EGFP/CA) and GagPol(MA/mSB/CA) containing mutations. HeLa cells were cotransfected with Gag(MA/EGFP/CA) plus GagPol(MA/mSB/CA) molecular clone containing CA mutations (W184A and M185A) or a deletion of the CA CTD (ΔCA CTD), NC (ΔNC), or SL1 and 3 (ΔSL1,3) at a DNA ratio of 1 : 1. A combination of Gag(MA/EGFP/CA) and soluble mSB was used as the negative control. WM > AA, W184A and M185A. The FRET efficiencies of the donor Gag–acceptor GagPol pairs were statistically greater than that of the negative control (P < 0.01). *Statistically significant (P < 0.01) compared with the wild‐type Gag(MA/EGFP/CA)–GagPol(MA/mSB/CA) pair. Representative FRET images are shown. (B) Virus particle production. HeLa cells were cotransfected with Gag(MA/EGFP/CA) and GagPol(MA/mSB/CA) molecular clones at a DNA ratio of 10 : 1. The particle fractions purified from the cell culture supernatants were analyzed by western blotting using a monoclonal antibody specific for HIV‐1 p24CA.
