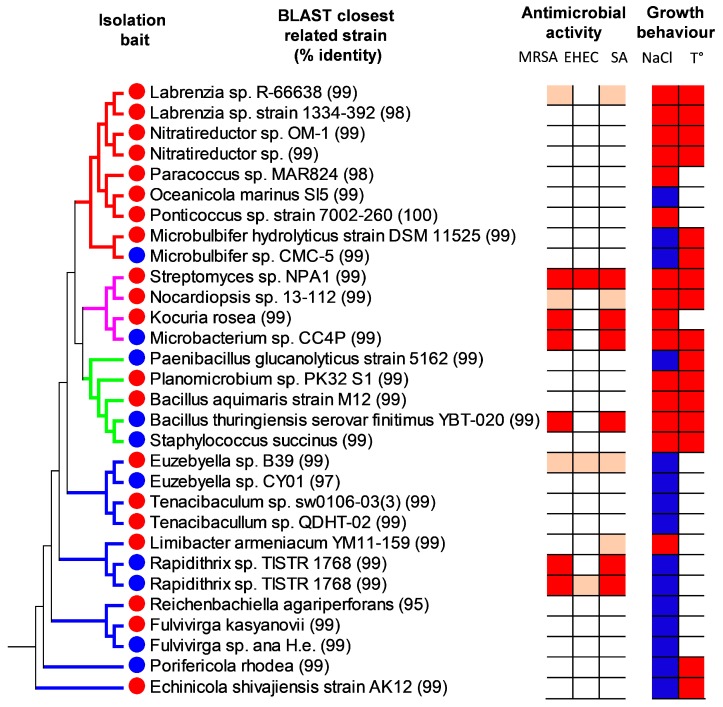
Figure 4.
Phylogenetic tree of antimicrobially active isolates. All of the strains indicated here showed activity against Arthrobacter psychrolactophilus. The color code of the tree branches indicates Proteobacteria (red), Actinobacteria (green), Firmicutes (purple), and Bacteroidetes (blue). The column “Isolation bait” indicates if the strain was isolated using E. coli (red), or P. inhibens (blue) as prey organism. Antimicrobial activity is given against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), enterohemorragic E. coli (EHEC), and methicillin-sensitive S. aureus (SA). Dark and light red indicate strong and moderate antimicrobial activity, respectively; white indicates that no activity was observed. Physiological properties of the strains are indicated on the right side. The NaCl column indicates if the strain is able to grow optimally with low NaCl concentration (<1%, red) or if it needs higher amounts (>1.5%, blue). The T° column indicates which strains were able to grow at an elevated temperature (40 °C). The 16S rRNA sequences of the strains have been deposited at GenBank with the accession numbers MF796603-MF796631 and MF620093.