Figure 5.
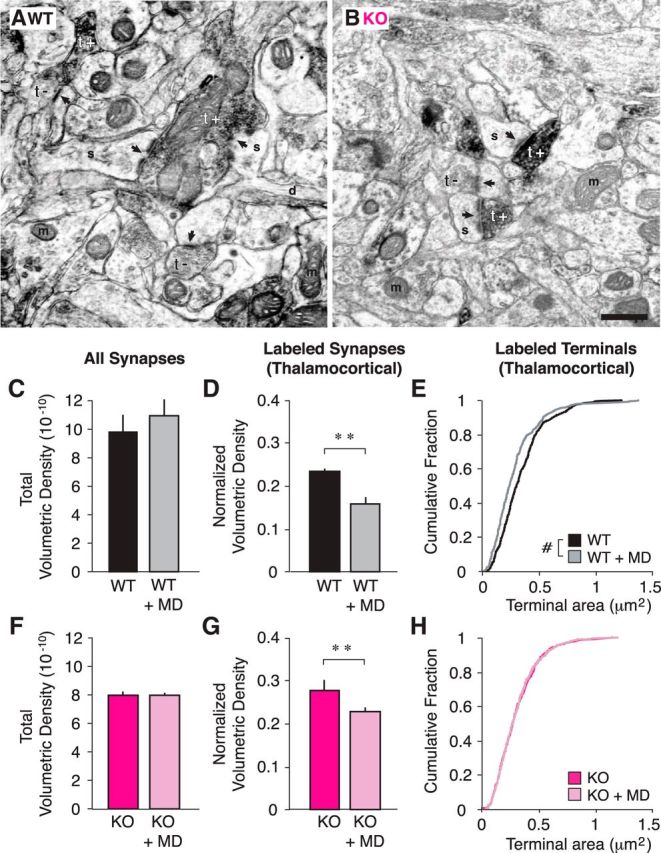
Thalamocortical synapses are less dense following brief MD in both WT and Cx3cr1 KO animals. A, B, Example EMs of WT (A) and KO (B) cortical slices. Synapses (arrows) are classified as originating from thalamic input based upon VGlut2 immunoreactivity (black, t+) or a lack of VGlut2 immunoreactivity (t−; s, spine; d, dendrite; m, mitochondria; scale bar, 500 μm). C, D, Total volumetric density of all synapses in WT animals is unchanged following MD (C; p > 0.05), but the normalized volumetric density of labeled synapses (Nvlabeled/Nvtotal) is significantly decreased (D; p = 0.005), as is the size of the terminals (E; p < 0.001). F, G, In KO animals, similar to WT animals, total volumetric density is unchanged after MD (F; p > 0.05) and normalized volumetric density of labeled synapses is decreased (G; p = 0.003). H, However, unlike WT brains, the size of labeled terminals is unaffected by MD in KO brains (p = 0.852; n = 3 WT, 3 WT+MD, 3 KO, and 6 KO+MD animals; terminal n = 489 WT, 381 WT+MD, 473 KO, 843 KO+MD; post hoc tests, **p < 0.01 after ANOVA; #p < 0.005, Mann–Whitney U test).
