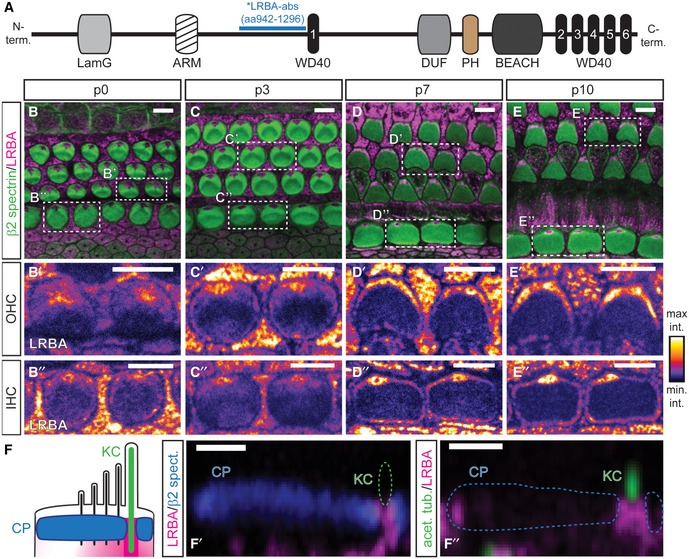
Developmental range (B–B″) p0, (C–C″) p3, (D–D″) p7, (E–E″) p10 showing LRBA clustering at a central position beneath the hair bundle in both, IHCs and OHCs. Samples were stained with specific antibodies against β2‐spectrin (green; cuticular plates) and LRBA (magenta) as well as fluorophore‐conjugated phalloidin (blue; stereocilia). Close‐ups of individual LRBA signals for (B′, C′, D′, E′) OHCs and (B″, C″, D″, E″) IHCs are presented in an intensity‐coded lookup table for clarity and show two adjacent hair cells surrounded by supporting cells as indicated in the dashed boxes in (B, C, D, E) (please also refer to
Appendix Fig S1C and D for
Lrba‐KO stainings, where all LRBA signal from hair cells and supporting cells is entirely lost). Scale bars: 5 μm.