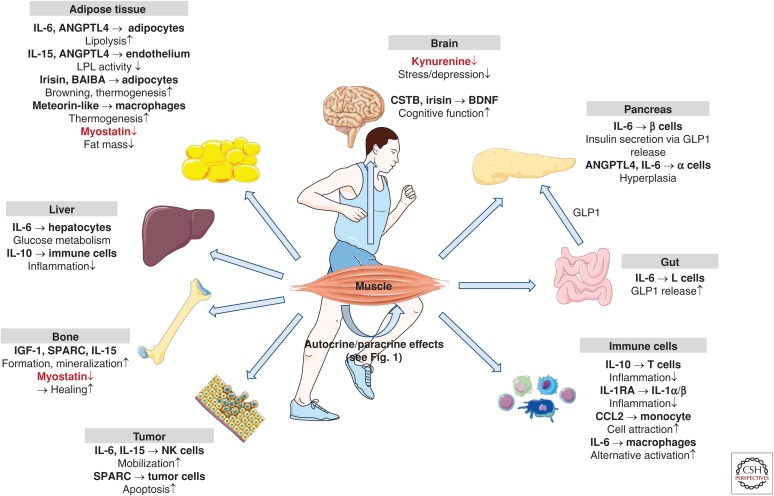
Figure 2.
Endocrine effects of exercise-regulated human myokines and metabolites. In addition to their autocrine and paracrine effects, myokines act on adipose tissue, liver, gut, brain, pancreas, bone, circulating and resident immune cells, and tumors. In most cases, exercise stimulates the release of myokines and metabolites (shown in black; BAIBA, β-amino isobutyric acid). Notable exceptions are myostatin and kynurenine, which are reduced after regular exercise (shown in red). (Figure created using illustrations provided by Servier Medical Art.)