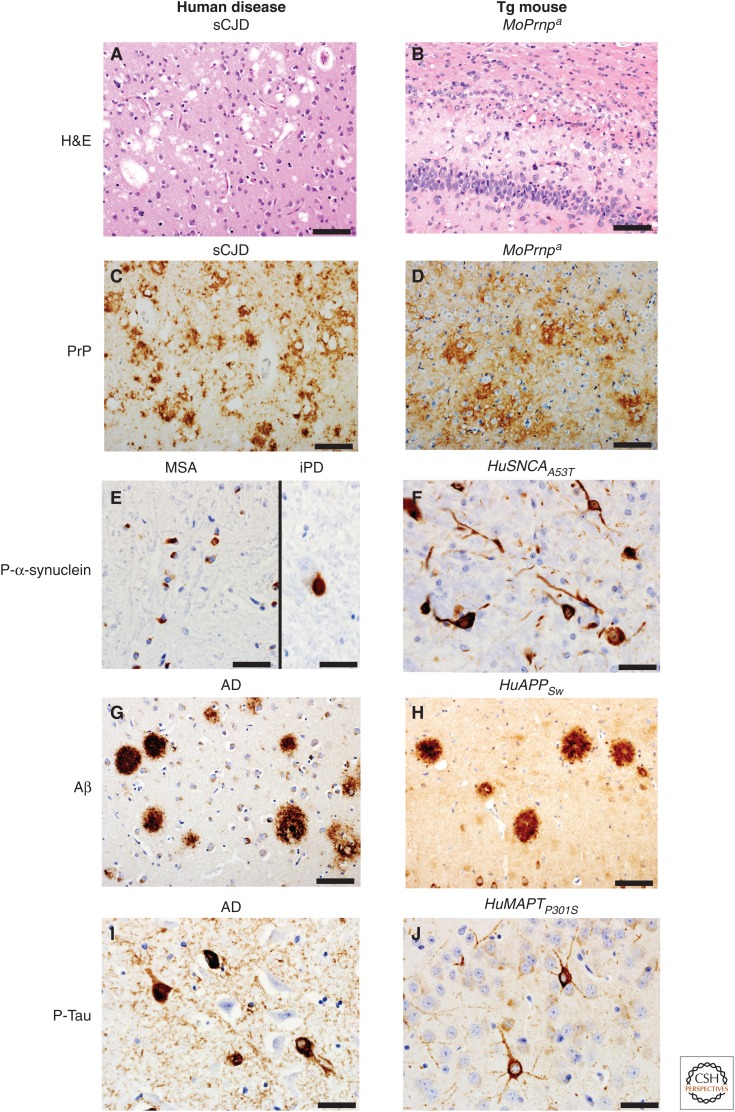
Figure 1.
Pathological hallmarks of select human neurodegenerative diseases (left) and those found in transgenic (Tg) mice expressing the protein involved in each disease listed above each panel (right). Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining reveals spongiform changes in the cortex of a 74-year-old sporadic Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease (sCJD) case (A) and in the hippocampus/corpus callosum of a Tg mouse (Tg4053 overexpressing mouse PrP-A) intracerebrally inoculated at 54 days of age with Rocky Mountain Laboratory (RML) prions euthanized at 114 days of age (B). Same mouse and human samples stained for prion protein (PrP) using immunohistochemistry (C,D, respectively). Immunohistochemistry for phosphorylated α-synuclein: (E) glial cytoplasmic inclusions in the putamen of a 66-year-old multiple system atrophy (MSA) case (left), and a Lewy body in the substantia nigra pars compacta of a 72-year-old incidental Parkinson’s disease (iPD) case (right); (F) intraneuronal accumulation within the cortex of a 110-d-old clinically ill transgenic α-synuclein mouse (M83 overexpressing SNCA with the A53T mutation) that was intracerebrally inoculated with brain homogenate from a 66-year-old MSA case different from the one shown. Amyloid-β (Aβ) immunohistochemistry of the parahippocampal area of a 73-year-old Alzheimer’s disease (AD) case (G) and an amyloid precursor protein gene (APP) mouse (APP23 overexpressing Swedish mutant human APP) euthanized at 688 days of age (H). Phosphorylated tau immunohistochemistry of the hippocampus of a 73-year-old AD case (I) and a clinically ill Tg tau mouse (Tg2541 overexpressing microtubule-associated protein tau [MAPT] with the P301S mutation) euthanized at 195 days of age (J). Scale bars, 50 µm (A–D,G–H); 20 µm (E,F,I,J).