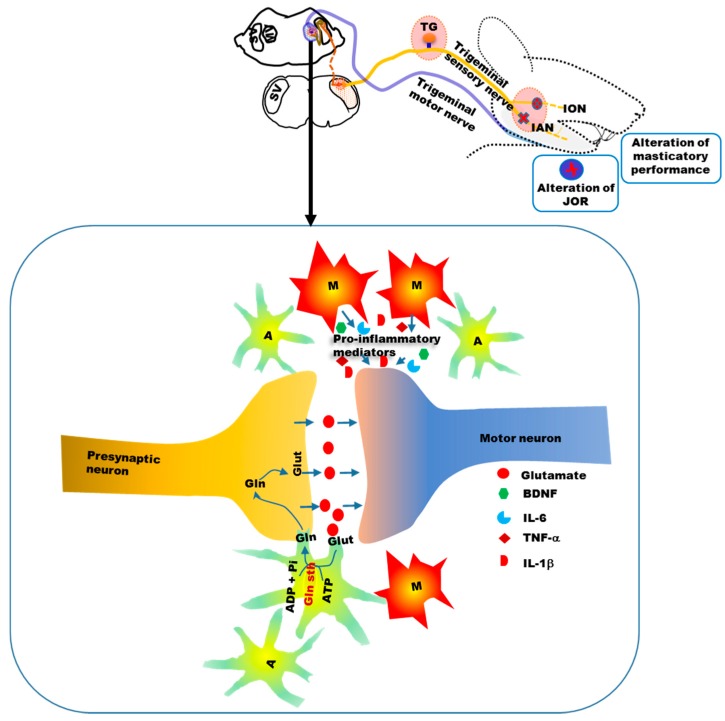
Figure 5.
Schematic showing the involvement of glia in the trigeminal motor nucleus in the change in orofacial motor activity following nerve injury. Activated microglia and astroglia are observed in the motor trigeminal nucleus following nerve injury. Similar to sensory nuclei, pro-inflammatory mediators might be released from hyperactive microglia, and these mediators may alter the sensitivity of motor neurons. The astroglial glutamate–glutamine shuttle might also participate in the modulation of motor neuronal activity. BDNF: Brain derived neurotrophic factor; IL-6: Interleukin 6; IL-1β: Interleukin 1 beta; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor alpha; Glut: Glutamate; Gln: Glutamine; Gln sth: glutamine synthetase; ADP: Adenosine Diphosphate; Pi: Inorganic phosphate; A: Astroglia; M: Microglia.