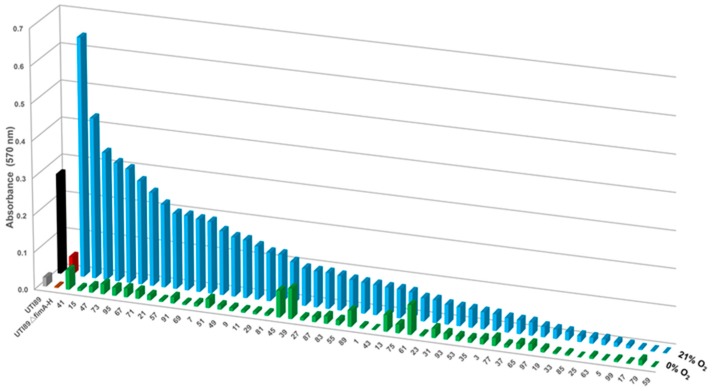
Figure 2.
The majority of urine-associated E. coli clinical isolates exhibit decreased biofilm formation under anoxic conditions independent of type 1 pili production. Graph depicting the quantified biomass for 50 urine-associated E. coli strains collected from the urine of patients at VUMC. These randomly-selected isolates were seeded in standard biofilm plates and allowed to develop biofilms along the wall of the wells for 48 h in ambient oxygen conditions. The Z-axis depicts the oxygen concentration under which the isolates were grown. Urine-associated E. coli isolates are graphed from the highest biofilm production to lowest under 21% oxygen (blue bars). UTI89 (black bars) and the isogenic UTI89∆fimA-H mutant (red bars) were used as controls for comparison of the assay. All isolates exhibited significantly-reduced biofilm compared to their own growth under ambient oxygen conditions, except isolates VUTI39 and VUTI61 (green bars). The average of a minimum of two independent experiments is shown, with a minimum of eight technical replicates per experiment. The standard error of the mean for each VUTI isolate is shown in Table S2.