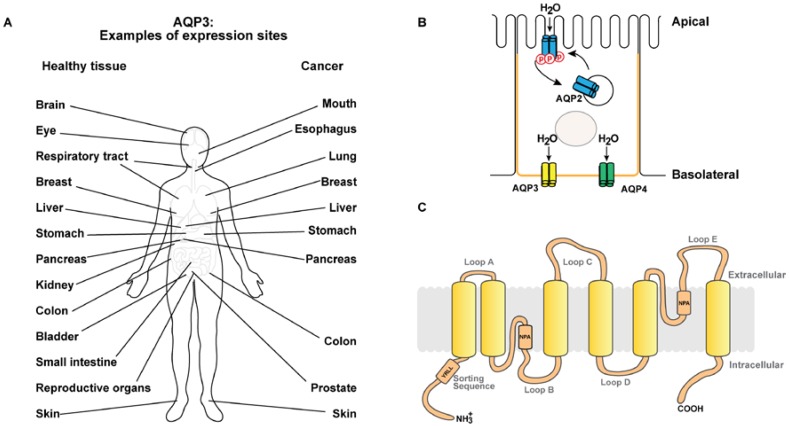
Figure 1.
Aquaporin-3 expression sites, subcellular localization, and topology. (A) Schematic showing examples of aquaporin-3 (AQP3) expression sites as well as examples of cancers, where increased expression of AQP3 has been reported. (B) Schematic of a kidney collecting duct principal cell. Transepithelial water transport is facilitated by apical AQP2 allowing entry of water into the collecting duct principal cell and AQP3 and AQP4 in the basolateral plasma membrane domain (orange), which facilitate exit of water. AQP2 plasma membrane localization is regulated by phosphorylation (denoted by p in the schematic) mediating shuttling between intracellular vesicles and the apical plasma membrane. (C) Schematic showing the topology of AQP3. Similar to other AQPs, AQP3 has six transmembrane domains and intracellular COOH and NH3+ termini. Two membrane-integrated helices with the conserved Asn-Pro-Ala (NPA) motifs generate the pore. AQP3 contains a basolateral sorting motif (YRLL) in the NH3+-terminal.