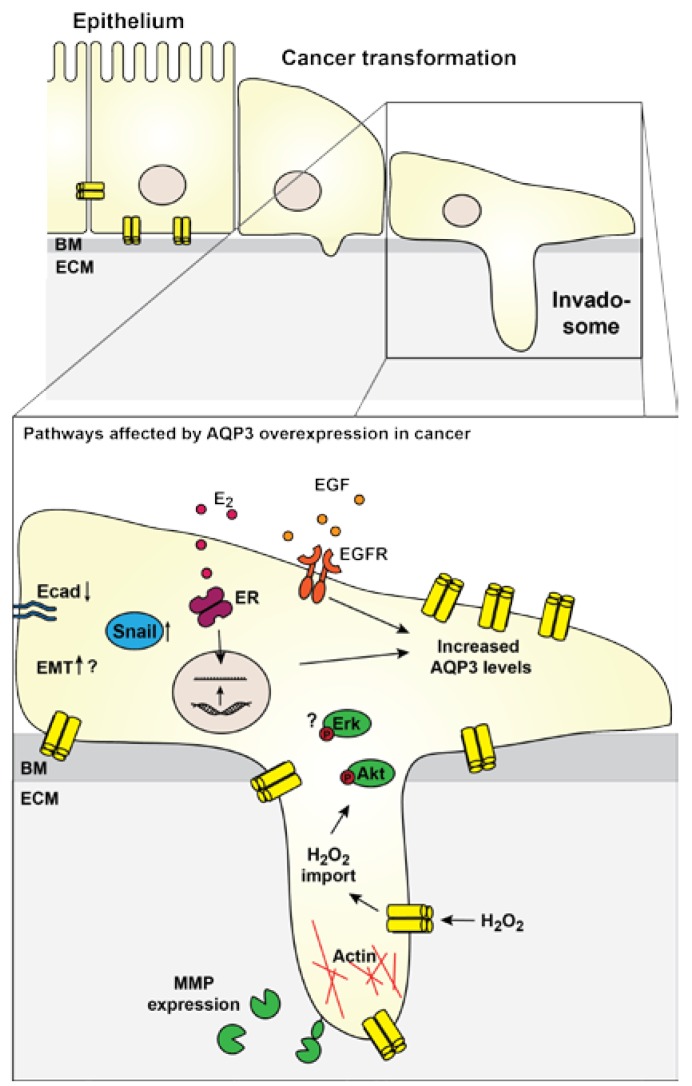
Figure 2.
Schematic showing signaling affecting AQP3 overexpression and the downstream effectors. In cancer, AQP3 is often upregulated. Upregulation may be stimulated by EGF signaling. Moreover, in ER-positive breast cancer, estrogen signaling increased AQP3 transcription. Some downstream effects of AQP3 in cancer have been identified or suggested. AQP3-mediated H2O2 uptake was necessary for increased protein kinase B (Akt) phosphorylation, and AQP3 may also affect extracellular signal-regulated kinase (Erk)1/2 phosphorylation through so far unknown mechanisms. AQP3 overexpression was necessary for increased expression of MMPs, which promote cancer cell invasiveness. Actin is polymerized in the leading edge of migrating cells, and AQP3 localizes here as well. AQP3 overexpression facilitated downregulation of E-cadherin and up-regulation of Snail suggesting a contribution of AQP3 to EMT. BM: Basement membrane; E2: Estradiol; Ecad: E-cadherin; ECM: Extra-cellular matrix; EGF: Epidermal growth factor; EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor; EMT: Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition; ER: Estrogen receptor; MMP: Matrix-metallo protease.