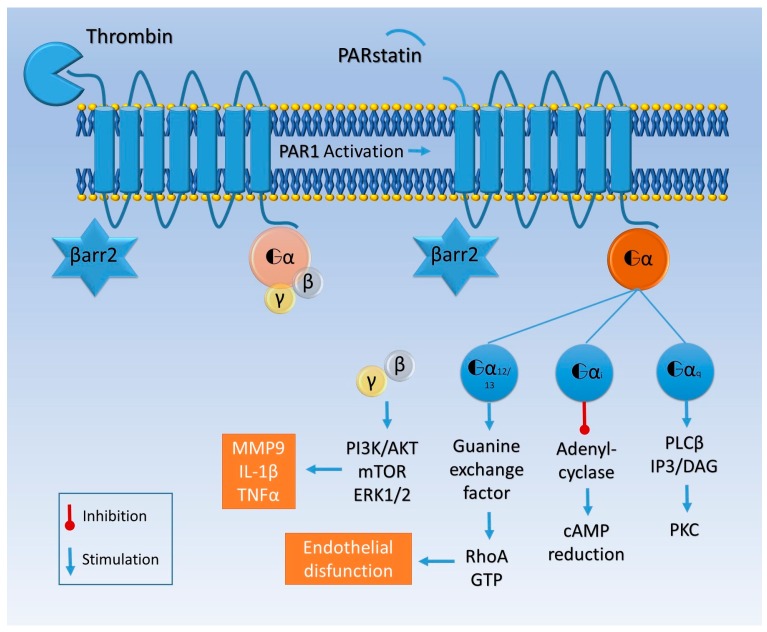
Figure 2.
Thrombin cleaves the amino-terminal domain of PAR1 and triggers intracellular signaling. The residual 41 amino acid peptide is called parstatin. PAR1 can be associated with Gαq, Gαi/o, or Gα12/13 proteins. Gαq activates phospholipase C β (PLC β), which catalyzes the formation of inositol trisphosphate (IP3) and diacylglycerol (DAG), which in turn activates protein kinase C (PKC). Gαi blocks adenylyl cyclase and reduces cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP). Gα12/13 is associated with guanine exchange factors and activates RhoA. βγ subunits activate the phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase (PI3K) pathway, leading to the production of MMP9, IL-1β, and TNFα. This is the “classic” PAR1 activation, and in this scenario β arrestin 2 (βarr2) remains inactive.