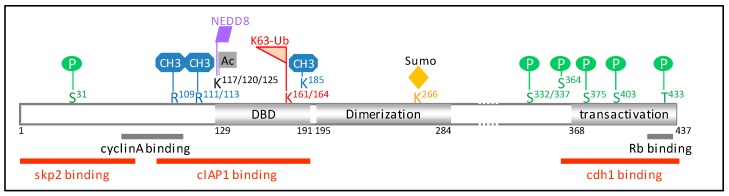
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of E2F1 protein sequence (NP_005216.1). The regions interacting with cyclin A, Rb (retinoblastoma), and the E3-ubiquitine ligases skp2 (S-phase kinase-associated protein 2), cIAP1 (cellular inhibitor of apoptosis 1), and cdh1 are shown. Amino acid residues involved in post-translational modifications are indicated. E2F1 is subjected to several post-translation modifications in response to genotoxic stress, including phosphorylation on S31 by the ataxia telangiectasia mutated/ataxia telangiestasia and Rad3-related (ATM/ATR) [37], on S364 by checkpoint kinase 2 (chk2) [38], methylation on K185 by Set7/9 [39,40], and on R109 by the protein arginine N-methyltransferase 1 (PRMT1) [41], demethylation on R111/113 [41], de-neddylation [42], and acetylation by the histone acetyl-transferase p300/CREB-binding protein-associated factor (P/CAF) on K117/120/125 [43,44] and K63-ubiquitination on K161/164 by cIAP1 [35]. The amino acid residues R111/113 are targets of methylation by PRMT5 [41,45], K117/120/125 of neddylation [46], K266 of sumoylation [47], S332/337 of phosphorylation by the cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (cdk1) [48], and S403/T433 by the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) [49]. DBD: DNA binding domain.